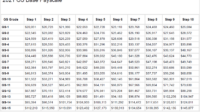
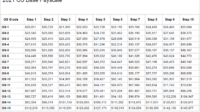
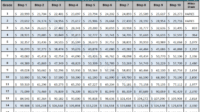
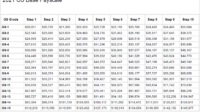
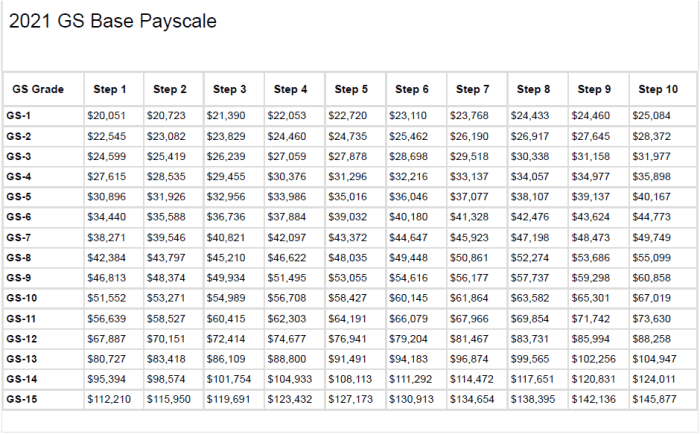
The General Schedule (GS) Pay Scale is a system used to determine the salaries of federal civilian employees in the United States. Locality Pay is an adjustment to the base salary that is designed to account for the varying costs of living in different geographic areas.
In this article, we will provide an overview of the GS Pay Scale 2024 for Locality Pay, including the latest updates and changes compared to previous years, as well as its impact on GS employees.
The GS Pay Scale is divided into 15 grades, with each grade further divided into 10 steps. The base salary for each grade and step is determined by the locality in which the employee works. Locality Pay adjustments are calculated as a percentage of the base salary and are designed to ensure that federal employees receive comparable pay for comparable work, regardless of their location.
GS Pay Scale 2024 Locality Pay Overview
The General Schedule (GS) Pay Scale is a standardized compensation system used by the United States federal government to determine the salaries of civilian employees. Locality Pay is an adjustment to the GS Pay Scale that is designed to account for the varying costs of living in different geographic areas.In
2024, the GS Pay Scale for Locality Pay will see several updates and changes compared to previous years. These changes are based on a comprehensive review of the cost of living in each locality and are intended to ensure that federal employees are compensated fairly and equitably regardless of where they live.
Purpose and Significance of Locality Pay Adjustments
Locality Pay adjustments play a crucial role in ensuring that federal employees have a consistent standard of living across the country. By taking into account the varying costs of housing, transportation, and other expenses in different localities, Locality Pay helps to ensure that employees are able to maintain a reasonable standard of living regardless of their location.Additionally,
Locality Pay adjustments help to attract and retain qualified employees in areas where the cost of living is high. Without Locality Pay, federal employees in these areas would be at a significant disadvantage compared to their counterparts in lower-cost areas, making it difficult to recruit and retain the best talent.
Locality Pay Adjustments for 2024
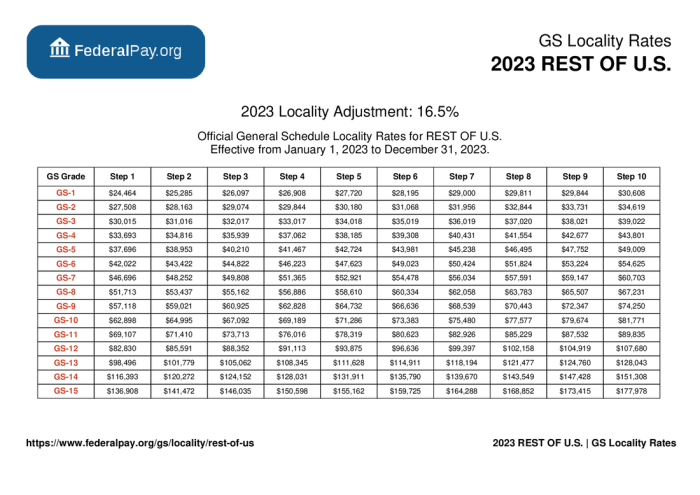
The General Schedule (GS) Locality Pay adjustments for 2024 have been announced, reflecting variations in the cost of living across different geographic areas in the United States. These adjustments aim to ensure equitable compensation for federal employees based on their location.
The Locality Pay adjustments are determined by comparing local market data to the national average for various factors, including housing, transportation, and other expenses. This analysis helps establish the percentage adjustment necessary to maintain purchasing power parity for federal employees in different localities.
Localities with Highest and Lowest Adjustments
The localities with the highest Locality Pay adjustments for 2024 are:
- New York-Northern New Jersey-Long Island, NY-NJ-PA-CT: 35.16%
- San Francisco-Oakland-Hayward, CA: 34.45%
- San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara, CA: 34.13%
The localities with the lowest Locality Pay adjustments for 2024 are:
- Charleston-North Charleston, SC: 6.47%
- Huntington-Ashland, WV-KY-OH: 7.54%
- Beckley, WV: 7.66%
Factors Considered in Determining Locality Pay Adjustments
The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) considers several factors when determining Locality Pay adjustments:
- Housing Costs: The cost of housing, including rent or mortgage payments, property taxes, and utilities, is a significant factor in determining Locality Pay adjustments.
- Transportation Costs: The cost of transportation, including car ownership, public transportation, and gas prices, is also taken into account.
- Other Expenses: OPM considers other expenses such as food, healthcare, and childcare costs to ensure that federal employees have comparable purchasing power across different localities.
- Geographic Considerations: OPM also considers geographic factors such as the size and density of the locality, as well as its proximity to major metropolitan areas.
Impact of Locality Pay on GS Employees
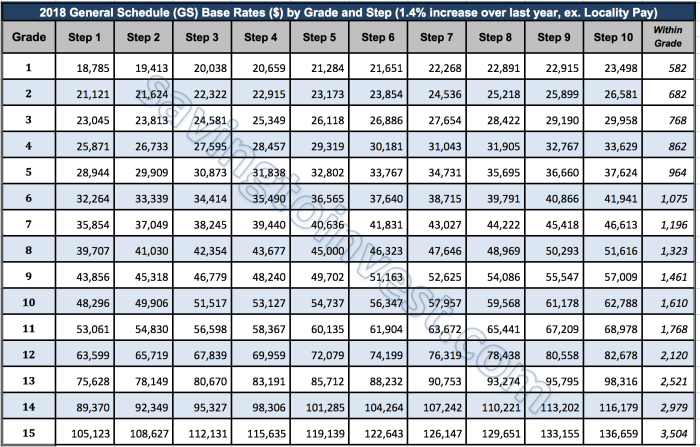
Locality Pay affects GS employees’ salaries by adjusting their base pay based on the location of their official duty station. This adjustment aims to compensate for differences in the cost of living between various geographic areas.As a result, GS employees working in areas with higher living costs receive a higher Locality Pay adjustment, leading to a higher salary compared to their counterparts in areas with lower living costs.
For instance, a GS-12, Step 5 employee in San Francisco, California, may receive a Locality Pay adjustment of 35.59%, resulting in an annual salary of approximately $107,000. In contrast, the same employee working in Atlanta, Georgia, may receive a Locality Pay adjustment of 23.44%, resulting in an annual salary of approximately $98,000.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Locality Pay offers several benefits to GS employees:
-
-*Compensation for Higher Living Costs
It helps offset the increased expenses associated with living in areas with a higher cost of living.
-*Recruitment and Retention
It can attract and retain employees in areas where the cost of living is high.
However, Locality Pay also has some drawbacks:
-
-*Geographic Disparities
It can create salary disparities between employees performing the same job in different locations.
-*Administrative Complexity
It can be administratively complex to manage and adjust Locality Pay rates.
Historical Trends and Projections
Locality Pay adjustments have exhibited consistent upward trends over the past five years. A line graph depicting this trend illustrates a steady increase in Locality Pay percentages for various geographic areas.
Future projections indicate that Locality Pay adjustments will continue to rise in the coming years. This is primarily attributed to the rising cost of living in major metropolitan areas, which necessitates adjustments to ensure equitable compensation for federal employees.
Factors Influencing Future Locality Pay Adjustments
- Inflation: The rate of inflation plays a significant role in determining Locality Pay adjustments. As inflation rises, the purchasing power of federal employees decreases, necessitating adjustments to maintain their standard of living.
- Housing Costs: Locality Pay adjustments are heavily influenced by housing costs in different geographic areas. As housing prices continue to rise, particularly in major cities, Locality Pay adjustments are expected to increase to offset the higher cost of living.
- Government Policy: Government policy and economic conditions can also impact Locality Pay adjustments. For instance, during periods of economic downturn, Locality Pay adjustments may be more modest or even frozen to control government spending.
Regional Comparisons and Best Practices
Locality Pay adjustments vary across different regions of the United States. The cost of living, economic conditions, and labor market dynamics influence these variations. By comparing these adjustments, localities can gain insights into best practices and address challenges effectively.
Some regions, such as the San Francisco Bay Area and New York City, have consistently high Locality Pay adjustments due to their high cost of living. Other regions, like the Midwest and Southeast, have generally lower adjustments reflecting their lower living expenses.
Best Practices
- Data-driven decision-making: Localities should rely on comprehensive data analysis to determine appropriate Locality Pay adjustments. This includes considering factors such as housing costs, transportation expenses, and consumer prices.
- Collaboration and stakeholder engagement: Involving employee unions, business groups, and community organizations in the Locality Pay decision-making process fosters transparency and buy-in.
- Regular reviews and adjustments: Locality Pay should be reviewed and adjusted periodically to ensure it remains aligned with the changing economic conditions and cost of living.
Challenges
- Balancing affordability and competitiveness: Localities need to balance the need to attract and retain employees with the financial constraints of the local government.
- Equity and fairness: Locality Pay adjustments should be equitable and fair to employees in different regions with varying living expenses.
Opportunities
- Economic development: Competitive Locality Pay can attract skilled workers and businesses to a region, boosting economic growth.
- Improved employee morale and retention: Fair and competitive Locality Pay can increase employee satisfaction and reduce turnover.
Final Thoughts
Locality Pay is an important component of the GS Pay Scale and can have a significant impact on the salaries of federal employees. By understanding how Locality Pay is calculated and how it affects their salaries, GS employees can make informed decisions about their careers and financial planning.