Navigating the complexities of federal employee salaries can be a daunting task. The 2024 GS Pay Scale Table serves as an essential tool for understanding the compensation structure and determining salaries for employees within the General Schedule (GS) system. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the table, exploring its significance, structure, and impact on employee earnings.
The GS Pay Scale Table establishes a standardized framework for determining salaries based on factors such as pay grades, step levels, and locality adjustments. Understanding these components is crucial for employees to accurately calculate their salaries and plan for their financial future within the federal workforce.
General Overview
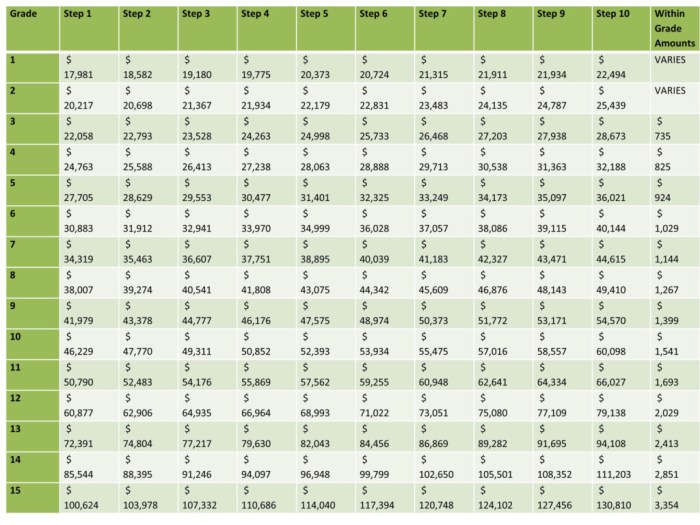
The 2024 GS Pay Scale Table serves as a comprehensive guide to the General Schedule (GS) pay system utilized by the United States federal government. This table establishes the salary ranges for various federal civilian positions, categorized by grade and step.The
significance of the GS Pay Scale Table lies in its role as the official reference for determining the salaries of federal employees. It ensures consistency and fairness in compensation across the federal workforce. The table is structured in an organized manner, with grades ranging from GS-1 to GS-15, and steps within each grade representing increments in experience and performance.
Structure and Organization
The 2024 GS Pay Scale Table comprises several columns, each providing specific information. The first column lists the grade and step, followed by columns displaying the annual salary ranges for each grade and step. Additionally, the table includes columns for locality pay adjustments, which account for differences in living costs across geographic regions.The
structure of the table allows for easy navigation and comparison of salary ranges across grades and steps. It provides a clear understanding of the pay scale for federal civilian positions and facilitates informed decision-making regarding career progression and compensation expectations.
Pay Grades and Step Levels
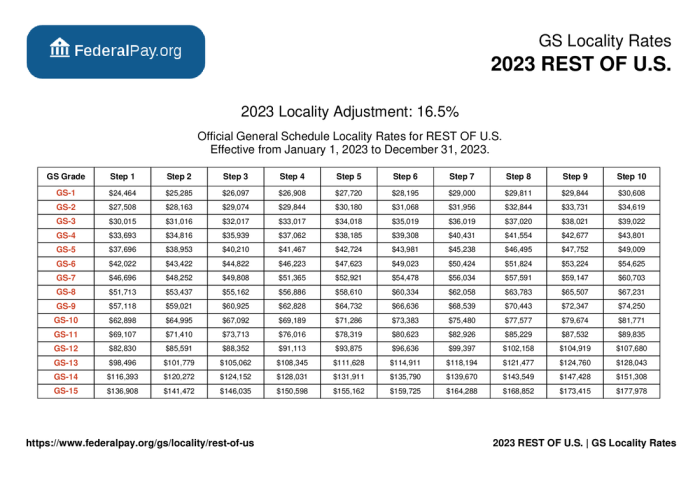
The 2024 GS Pay Scale Table comprises a range of pay grades and step levels that determine the salaries of federal employees. These pay grades and step levels form the basis for calculating employee compensation, with higher pay grades and step levels corresponding to higher salaries.
The GS Pay Scale Table consists of 15 pay grades, each of which is further divided into 10 step levels. Pay grade refers to the broad job classification, while step level represents an employee’s seniority and performance within that grade.
Pay Grades
The 15 pay grades are designated by numbers from GS-1 to GS-15. Each pay grade encompasses a specific range of job responsibilities and levels of experience. Higher pay grades are typically associated with more complex and demanding roles.
Step Levels
Within each pay grade, there are 10 step levels, denoted by numbers from 1 to 10. Step levels indicate an employee’s relative seniority and performance within their pay grade. Employees typically advance through step levels over time based on satisfactory job performance and experience.
Relationship Between Pay Grades, Step Levels, and Salaries
The combination of pay grade and step level determines an employee’s salary. The higher the pay grade and step level, the higher the salary. Salaries are calculated using a formula that incorporates the base pay for the employee’s pay grade and step level, as well as locality adjustments based on the employee’s geographic location.
Example
For instance, an employee in pay grade GS-11, step level 5, working in the Washington, D.C. metropolitan area, would have a base salary of $72,826 per year. This salary includes a locality adjustment of 29.93%, which is applied to the base pay for employees in the Washington, D.C.
area.
Locality Pay Adjustments
Locality pay adjustments are designed to address the varying costs of living across different geographic areas. These adjustments aim to ensure that federal employees receive comparable compensation regardless of their location.
Locality pay adjustments are determined by comparing the cost of living in a particular locality to the cost of living in the Washington, D.C., metropolitan area. The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) conducts regular surveys to gather data on housing, transportation, food, and other expenses.
Geographic Coverage
Locality pay adjustments are applied to federal employees in designated geographic areas known as “locality pay areas.” These areas are typically metropolitan areas or counties with a high concentration of federal employees.
Impact on Salaries
Locality pay adjustments can have a significant impact on an employee’s salary. For example, an employee in a high-cost-of-living area may receive a locality pay adjustment of 20%, while an employee in a low-cost-of-living area may receive an adjustment of only 5%.
The following table shows how locality pay adjustments can affect an employee’s salary:
| Base Salary | Locality Pay Adjustment | Total Salary |
|---|---|---|
| $50,000 | 20% | $60,000 |
| $50,000 | 5% | $52,500 |
Special Rates of Pay
Special rates of pay are additional compensation provided to federal employees in specific situations or for performing specific duties. These rates are designed to compensate employees for unique working conditions, hazardous work, or other special circumstances.Eligibility for special rates of pay is determined by the employee’s job duties, location, and other factors.
Employees must meet specific criteria to qualify for these rates, which are typically Artikeld in agency regulations or collective bargaining agreements.
Application Process
To apply for special rates of pay, employees typically submit a written request to their supervisor or human resources department. The request should include documentation supporting the employee’s eligibility for the rate. The agency will then review the request and determine whether to approve the rate.
Examples of Special Rates of Pay
Common examples of special rates of pay include:
-
-*Overtime pay
Paid for hours worked beyond the standard 40-hour workweek.
-*Holiday pay
Paid for holidays designated by the federal government.
-*Night differential
Paid for work performed during designated night hours.
-*Hazard pay
Paid for work in hazardous or dangerous conditions.
-*Environmental differential pay
Paid for work in areas with extreme environmental conditions.
Potential Impact on Salaries
Special rates of pay can significantly impact employee salaries. For example, an employee who works overtime may receive a higher salary than an employee who does not.
Similarly, an employee who works in a hazardous environment may receive a higher salary than an employee who does not.
5. Table Design and Accessibility
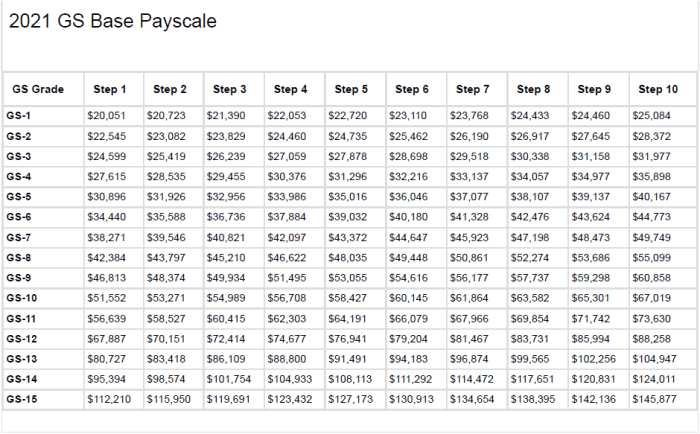
To ensure clarity and accessibility, the 2024 GS Pay Scale Table is presented in an HTML table format.
The table is designed to be responsive, allowing it to be viewed comfortably on various devices. It incorporates appropriate headings, labels, and formatting to enhance readability.
Table Structure
- The table is organized into columns representing Pay Grades and Step Levels.
- Each cell contains the corresponding salary amount for the specific Pay Grade and Step Level.
- The table is sortable by clicking on the column headers, allowing users to easily compare salaries across different Pay Grades and Step Levels.
6. Historical Context
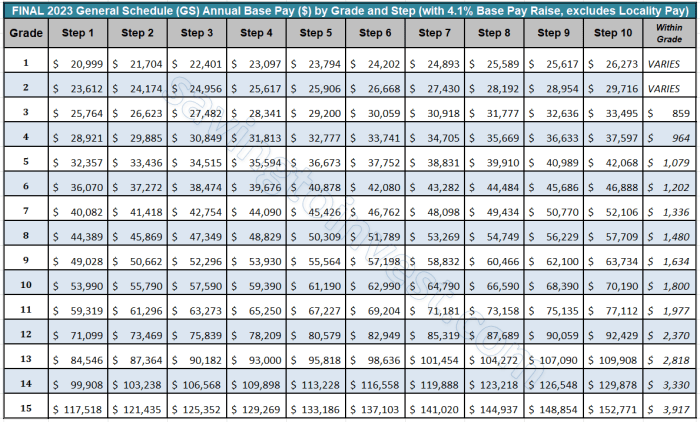
The General Schedule (GS) Pay Scale Table has undergone several changes and revisions throughout its history, reflecting the evolving needs of the federal workforce and the economic landscape.
The table was first established in 1949 under the Classification Act of 1949. It aimed to provide a standardized pay structure for federal employees, ensuring fair and equitable compensation across different agencies and job classifications.
Major Revisions
- 1972: The Pay Comparability Act of 1970 led to significant revisions in the GS Pay Scale Table, including the addition of locality pay adjustments to address regional differences in the cost of living.
- 1982: The Federal Employees Pay Comparability Act of 1982 made further adjustments to the table, including the introduction of special rates of pay for certain occupations and locations.
- 1990: The Federal Employees Pay Comparability Act of 1990 introduced a new pay system based on performance, known as the Performance Management and Recognition System (PMRS).
- 2013: The Pay Equity and Transparency Act of 2013 brought about additional changes, including the requirement for agencies to conduct pay equity audits and make adjustments as necessary.
Closing Summary
The 2024 GS Pay Scale Table is a dynamic document that reflects the evolving needs of the federal workforce and the economic landscape. By staying informed about the latest updates and changes to the table, employees can ensure they receive fair and equitable compensation for their contributions to the government.
This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the table, empowering readers with the knowledge they need to navigate the federal salary system effectively.


