GS Pay for New Hires: Starting Salaries Demystified takes center stage, and we’re about to embark on a journey to uncover the secrets behind those initial paychecks. Navigating the world of salaries can feel like a maze, especially for fresh graduates or those new to a company.
But fear not, because we’re here to provide clarity and insight into how GS determines starting salaries for its new hires. From understanding the factors that influence those initial offers to exploring the benefits and perks that come with joining the GS team, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to confidently navigate the salary discussion.
This guide will explore the intricacies of GS’s salary structure, highlighting the key factors that influence starting salaries. We’ll delve into the role of experience, education, location, and even performance potential in shaping those initial paychecks. We’ll also take a closer look at specific salary ranges for various entry-level roles, providing a clear picture of what you can expect based on your chosen career path.
And because we believe in empowering you to make informed decisions, we’ll share valuable tips for negotiating your starting salary, ensuring you receive fair compensation for your skills and experience.
GS Pay for New Hires
The General Schedule (GS) pay system is a standardized pay structure used by the United States federal government to determine the salaries of its employees. Understanding this system is crucial for anyone seeking a career within the federal government, especially new hires.
This guide provides an overview of the GS pay structure and the factors that influence starting salaries for new hires.
Factors Influencing Starting Salaries
The starting salary for a GS position is determined by a combination of factors, including:
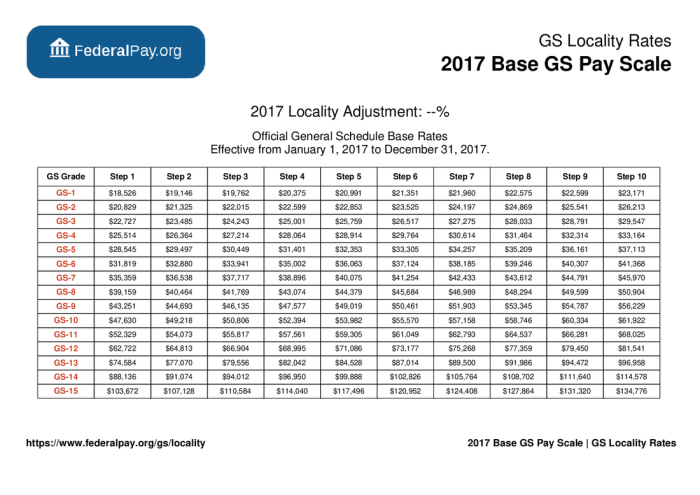
- Grade Level:The GS grade level reflects the complexity, difficulty, and responsibility of the position. Higher grade levels correspond to more senior positions and higher salaries. For example, a GS-5 position is a lower-level entry-level position, while a GS-15 position is a highly specialized and senior-level position.
- Step:Within each grade level, there are 10 steps, representing incremental increases in pay. New hires typically start at Step 1, but their starting step may be higher based on their experience and qualifications.
- Location:Salaries for GS positions vary based on the location of the job. The federal government has established different “pay areas” across the country, with higher pay areas generally reflecting higher costs of living.
- Experience and Qualifications:The more experience and qualifications a new hire possesses, the higher their starting salary is likely to be. This may include relevant education, certifications, or prior work experience in the field.
GS Salary Bands and Levels for New Hires
The GS pay system is organized into different salary bands, or levels, for new hires. These bands are based on the grade level and step of the position:
| Grade Level | Starting Salary (Step 1) |
|---|---|
| GS-1 | $21,000
|
| GS-2 | $24,000
|
| GS-3 | $27,000
|
| GS-4 | $30,000
|
| GS-5 | $33,000
|
Note: These salary ranges are estimates and can vary depending on the specific location, experience, and qualifications of the new hire. The actual salary for a GS position is determined by the Office of Personnel Management (OPM).
Key Factors Influencing Starting Salaries
The starting salary for a GS position is influenced by several key factors. These factors encompass an individual’s qualifications, experience, location, and the specific demands of the position.
Experience
Experience plays a crucial role in determining starting salaries for GS positions. The more experience an individual has in a relevant field, the higher their starting salary is likely to be. This is because experience demonstrates competence, knowledge, and the ability to contribute effectively to the organization.
For example, a candidate with five years of experience in a specific field may command a higher starting salary than a candidate with one year of experience, even if they hold the same qualifications.
Education and Qualifications
Education and qualifications are essential factors in determining starting salaries for GS positions. A higher level of education, such as a Master’s degree or PhD, often leads to a higher starting salary. This is because advanced degrees indicate specialized knowledge and skills that are valuable to organizations.
Additionally, specific certifications or licenses may also increase starting salaries, as they demonstrate expertise in a particular area. For example, a candidate with a Master’s degree in engineering and a professional engineering license may receive a higher starting salary than a candidate with a Bachelor’s degree in engineering.
Location and Cost of Living
Location and cost of living are significant factors in determining starting salaries for GS positions. GS positions in major metropolitan areas, where the cost of living is higher, typically offer higher starting salaries to compensate for the increased expenses.
For example, a GS position in New York City may have a higher starting salary than a similar position in a smaller city, like Omaha, Nebraska. This is because the cost of housing, transportation, and other necessities is significantly higher in New York City.
The mystery of GS pay for new hires can be unveiled by understanding the intricate web of salary scales. For those seeking a career in human resources, navigating this complex landscape is crucial. Delve deeper into the intricacies of the GS Pay Scale with a comprehensive guide, GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources: A Comprehensive Guide , to unlock the secrets of starting salaries and pave your path to a rewarding career.
Performance and Potential
Performance and potential play a role in salary negotiations for GS positions. Candidates who demonstrate exceptional performance in their previous roles, such as high achievement in their studies or significant contributions to previous employers, may be able to negotiate higher starting salaries.
Similarly, candidates who possess strong potential for future growth and development may also be able to command higher salaries. This is because organizations recognize the value of investing in individuals with high potential and are willing to offer competitive salaries to attract and retain them.
Benefits and Perks for New Hires: GS Pay For New Hires: Starting Salaries Demystified
GS recognizes the importance of attracting and retaining top talent, and its comprehensive benefits package reflects this commitment. The company offers a wide range of benefits and perks to its new hires, designed to support their well-being, financial security, and overall work-life balance.
Health Insurance
GS offers a comprehensive health insurance plan that covers medical, dental, and vision care. This plan is designed to provide employees with access to quality healthcare services and peace of mind. The company also offers flexible spending accounts (FSAs) for healthcare and dependent care expenses, allowing employees to set aside pre-tax dollars to pay for eligible expenses.
Unravel the enigma of GS pay for new hires, where starting salaries can seem like a cryptic code. Dive into the intricacies of the GS pay scale, a labyrinth of classifications and steps, with Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals , a beacon of clarity in this bureaucratic maze.
This guide will illuminate the path to understanding your potential earnings, helping you navigate the treacherous terrain of GS pay and emerge with a clear vision of your starting salary.
Retirement Plans
GS provides its employees with a 401(k) plan, allowing them to save for retirement and receive company matching contributions. The company also offers a defined benefit pension plan, providing employees with a guaranteed stream of income after retirement. These plans are designed to help employees build a secure financial future.
Paid Time Off
GS offers a generous paid time off (PTO) policy, allowing employees to take time off for vacation, personal needs, or sick leave. The company also provides paid holidays, allowing employees to enjoy time with their families and friends. This policy promotes work-life balance and allows employees to recharge and return to work refreshed.
The labyrinthine world of GS Pay for new hires can seem daunting, especially when deciphering the starting salary intricacies. But fear not, aspiring administrative assistants, for a beacon of clarity shines in the form of Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrative Assistants.
This guide unveils the secrets of the GS Pay Scale, empowering you to confidently navigate the salary landscape and claim your rightful place in the administrative world.
Other Perks
In addition to the standard benefits, GS offers a variety of unique perks to its employees. These include:
- Employee discounts on various products and services
- Tuition reimbursement programs for continuing education
- Employee assistance programs (EAPs) for mental health and well-being
- On-site fitness centers and wellness programs
- Employee recognition programs and awards
These perks are designed to enhance the employee experience and create a positive and supportive work environment.
Tips for Negotiating Salary
Negotiating your starting salary at GS can be a daunting task, but with the right approach, you can secure a fair and competitive compensation package. It’s crucial to be well-prepared, confident, and assertive during the negotiation process.
Researching Industry Standards and Company Compensation Policies
Thorough research is essential before engaging in any salary negotiation. Knowing the market value for your skills and experience in your field is crucial. Online resources like Glassdoor, Salary.com, and PayScale can provide valuable insights into salary ranges for similar roles at GS and other companies in your industry.
Additionally, reviewing GS’s compensation philosophy and policies can provide valuable information about their approach to salary determination. This research will help you understand the company’s perspective and formulate a realistic and justified salary expectation.
Highlighting Skills and Experience During Salary Negotiations, GS Pay for New Hires: Starting Salaries Demystified
Effectively communicating your value proposition is crucial during salary negotiations. Highlighting your relevant skills, experience, and accomplishments that align with the requirements of the role is essential. Quantify your achievements whenever possible, providing specific examples of your contributions and impact.
For instance, if you have a proven track record of exceeding sales targets, highlight the percentage by which you exceeded those targets and the positive impact it had on the company’s revenue. Be prepared to articulate how your skills and experience will benefit GS and contribute to their success.
Resources for Salary Information
It’s crucial for new hires to understand the salary structure and potential earnings within the GS pay scale. This information can help you negotiate your salary effectively and make informed decisions about your career path.
Government Websites
Government websites are the most reliable sources for information about GS pay scales. They provide official salary tables, pay rates, and details about various pay adjustments and bonuses.
- Office of Personnel Management (OPM):The OPM website provides comprehensive information about the GS pay scale, including salary tables, locality pay adjustments, and other relevant resources. [link: https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/salaries-wages/]
- Federal Pay Schedule:The Federal Pay Schedule provides detailed information about the GS pay scale, including salary ranges for each grade and step. [link: https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/salaries-wages/2023-federal-pay-schedule/]
- Agency Websites:Most federal agencies have dedicated sections on their websites that provide information about salaries and compensation for their employees. You can find details about specific job titles, salary ranges, and other relevant information.
Salary Databases and Websites
Several online resources offer salary data and insights, including those specific to the government sector. These websites can help you compare salaries across different agencies and job titles.
- Glassdoor:This website allows you to search for salaries based on job title, location, and company. It also provides insights into company culture and employee reviews. [link: https://www.glassdoor.com/]
- Indeed:Similar to Glassdoor, Indeed offers salary information based on job title and location. It also provides job postings and company reviews. [link: https://www.indeed.com/]
- Salary.com:This website offers a comprehensive salary database with information on various job titles, industries, and locations. [link: https://www.salary.com/]
Industry Reports and Publications
Industry reports and publications often provide valuable insights into salary trends and compensation practices within the government sector.
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS):The BLS publishes detailed reports on wages and employment trends across various industries, including the public sector. [link: https://www.bls.gov/]
- Government Executive:This publication provides news and analysis on government issues, including compensation and benefits. [link: https://www.govexec.com/]
- Federal Times:This publication focuses on news and information related to the federal government, including salary and benefits information. [link: https://www.federaltimes.com/]
Internal GS Resources
Many federal agencies offer internal resources for salary information, including:
- Human Resources (HR) Department:The HR department within your agency can provide you with specific information about the GS pay scale, salary ranges for your job title, and any relevant pay adjustments or bonuses.
- Employee Handbooks:Agency employee handbooks often include information about salaries, compensation, and benefits.
- Union Representatives:If your agency has a union, union representatives can provide you with information about salary negotiations and other relevant issues.
Summary
As you step into the world of GS, remember that your starting salary is just the beginning of a potentially rewarding journey. By understanding the factors that influence pay, researching industry standards, and confidently navigating the salary negotiation process, you’ll be well-equipped to secure a fair and competitive starting salary that reflects your value.
With the right knowledge and preparation, you can embark on a fulfilling career path at GS, knowing that you’re being compensated fairly for your contributions.


