Mastering the GS Pay Calculator: Tips and Tricks – Let’s face it, deciphering the world of government pay can feel like navigating a labyrinth of numbers and acronyms. But fear not, dear reader! This guide will equip you with the tools and knowledge to confidently calculate your potential salary, understand those pesky pay adjustments, and even use the calculator for career planning.
We’ll demystify the process, making it as clear as a crisp dollar bill.
Imagine a world where you can effortlessly calculate your government salary, anticipate future pay increases, and make informed decisions about your career path. This is the power of the GS Pay Calculator. It’s your secret weapon for navigating the intricacies of government compensation and achieving your financial goals.
Understanding the GS Pay Calculator
The GS Pay Calculator is a valuable tool for federal employees and potential applicants to understand their potential salary. It helps determine the salary based on various factors like pay grade, step, locality pay, and deductions.
Components of the GS Pay Calculator
The GS Pay Calculator uses several components to calculate an employee’s salary. Understanding these components is crucial for accurately using the calculator.
- Pay Grade:This represents the level of responsibility and experience required for a specific position. It ranges from GS-1 to GS-15, with higher grades indicating more senior roles.
- Step:Within each pay grade, there are 10 steps. Each step signifies a year of experience and increased salary. Employees progress through steps based on performance and time in service.
- Locality Pay:This adjustment is added to the base salary depending on the location of the job. It reflects the cost of living in different areas.
- Deductions:These are amounts subtracted from the gross salary for taxes, retirement contributions, health insurance, and other benefits.
Using the GS Pay Calculator
The GS Pay Calculator is easy to use. You simply need to input the following information:
- Pay Grade:Enter the appropriate grade for the position.
- Step:Enter the corresponding step based on the employee’s experience.
- Locality Pay:Select the location of the job to determine the applicable locality pay.
The GS Pay Calculator will then automatically calculate the employee’s gross salary, considering the base salary, locality pay, and any applicable deductions.
Mastering the GS Pay Calculator requires understanding the intricacies of the federal pay system. To effectively navigate this system, it’s essential to have a firm grasp of the latest pay scales, especially for those in Human Resources. A comprehensive guide to the GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources can be an invaluable resource.
By familiarizing yourself with these scales, you can better predict potential salary ranges, understand the impact of locality pay, and make informed decisions regarding compensation strategies.
For example, let’s say a federal employee works in Washington, D.C., at a GS-9 position with 5 years of experience. Using the GS Pay Calculator, you would enter:
- Pay Grade:GS-9
- Step:5 (assuming 5 years of experience)
- Locality Pay:Washington, D.C.
The calculator will then display the employee’s estimated salary, taking into account the base salary, locality pay, and any applicable deductions.
Navigating the GS Pay Calculator Website
The GS Pay Calculator website is a valuable tool for federal employees and those considering a career in the federal government. Navigating this website is straightforward and intuitive, allowing you to quickly find the information you need.
Accessing the GS Pay Calculator Website
The GS Pay Calculator website is readily available online. To access it, follow these steps:
- Open your preferred web browser.
- In the address bar, type “OPM GS Pay Calculator” or visit the official website of the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) at “https://www.opm.gov/”.
- On the OPM website, navigate to the “Pay & Leave” section.
- Locate and click on the “GS Pay Calculator” link. This will take you to the GS Pay Calculator website.
Search Options on the GS Pay Calculator Website
The GS Pay Calculator website provides various search options to help you find the information you need. These options include:
- Location: This option allows you to search for pay rates based on the specific location where you are employed or plan to work. You can enter a city, state, or zip code.
- Grade and Step: This option enables you to find the pay rate for a specific GS grade and step. You can select the grade and step from the dropdown menus.
- Pay Table: The GS Pay Calculator website offers pay tables for different pay periods. You can select the pay table you are interested in.
Key Features of the GS Pay Calculator Website
The GS Pay Calculator website offers a range of features designed to make it user-friendly and informative.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| User-Friendly Interface | The website is designed with a simple and intuitive interface, making it easy to navigate and use. |
| Comprehensive Data | The GS Pay Calculator provides accurate and up-to-date information on GS pay rates for all grades and steps. |
| Multiple Search Options | The website offers various search options, including location, grade and step, and pay table, to help you find the information you need quickly. |
| Printable Results | You can easily print the results of your search for your records or to share with others. |
Calculating Your Potential Salary
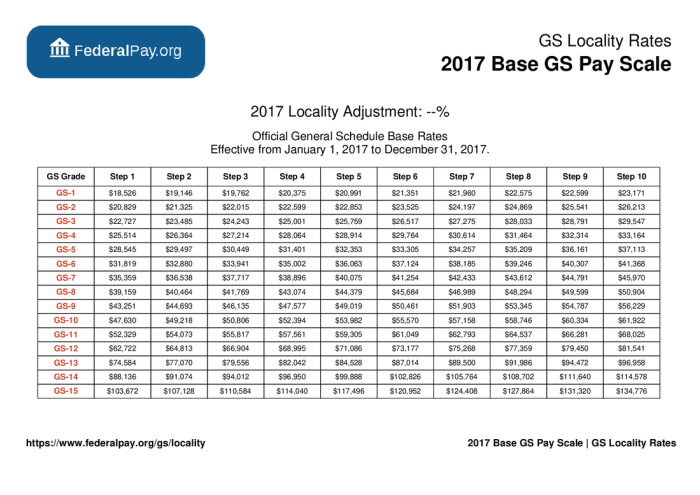
The GS Pay Calculator is a powerful tool that allows you to estimate your potential salary based on your experience, location, and grade level. It’s an essential resource for anyone considering a federal government job, as it provides a clear picture of what you can expect to earn.
Mastering the GS Pay Calculator is essential for administrative assistants, as it helps you understand your potential earnings based on your grade and step. To navigate the complexities of the GS Pay Scale 2024, a comprehensive guide for administrative assistants can be found here.
With a thorough understanding of the GS Pay Scale, you can effectively utilize the calculator to determine your salary expectations and negotiate fair compensation.
Entering Employee Information
The calculator requires specific information about your employment to provide an accurate salary estimate. This information includes:
- Grade Level:This refers to your position’s level of responsibility and complexity, ranging from GS-1 to GS-15.
- Step:This indicates your level of experience within your grade level. Each grade has 10 steps, with higher steps representing more experience.
- Location:The calculator requires you to select the specific location where you will be employed. This is important because salaries vary depending on the cost of living in different areas.
- Pay Table:The GS Pay Calculator uses a pay table to determine the salary for a specific grade, step, and location. There are different pay tables for different types of employees, such as those in the General Schedule, the Foreign Service, and the Senior Executive Service.
Adjusting Calculator Settings
The GS Pay Calculator allows you to adjust settings to reflect specific circumstances. For example, you can:
- Adjust the Pay Table:If you are a member of a different pay table, such as the Foreign Service or the Senior Executive Service, you can select the appropriate pay table to obtain a more accurate salary estimate.
- Include Locality Pay:Locality pay is an additional payment that is added to the base salary for employees working in certain areas with a high cost of living. The calculator allows you to include locality pay in your calculations.
- Factor in Bonuses:Some federal employees are eligible for performance bonuses. The calculator can incorporate bonuses into your salary estimate.
Interpreting Salary Results
Once you have entered your information and adjusted the settings, the calculator will provide you with an estimated salary range. This range represents the minimum and maximum possible salary for your position, based on the factors you have entered.
The estimated salary range is not a guarantee of your actual salary. It is a starting point for negotiations with your potential employer.
The salary range is also affected by other factors, such as your experience, qualifications, and performance. The calculator provides a valuable starting point, but it is important to consider all relevant factors when determining your salary expectations.
Understanding Pay Adjustments and Increases
The GS Pay Calculator is a valuable tool for understanding your potential salary, but it’s crucial to consider the various pay adjustments and increases that can impact your earnings. These adjustments are not reflected in the base GS pay scale and can significantly influence your final salary.
Types of Pay Adjustments
Pay adjustments are changes to your base salary that are made on a regular basis or due to specific circumstances. The two most common types of pay adjustments are step increases and locality pay adjustments.
- Step Increases:These are automatic increases in your salary based on your time in service and performance. Every year, you move to the next step within your pay grade, receiving a corresponding salary increase. The amount of the increase varies depending on the step you’re moving to.
For instance, the increase from Step 1 to Step 2 is typically larger than the increase from Step 9 to Step 10.
- Locality Pay Adjustments:These adjustments are made to account for differences in the cost of living across different geographic locations. They are applied to GS employees in certain metropolitan areas and are intended to ensure that employees in high-cost areas receive a competitive salary.
The locality pay adjustment is a percentage of the base GS pay, and it varies depending on the location. For example, employees in New York City might receive a higher locality pay adjustment than employees in a rural area.
Factors Influencing Pay Adjustments and Increases
Several factors can influence pay adjustments and increases, including:
- Time in Service:Your time in service is a key factor in determining step increases. The longer you’ve been employed, the higher your step and salary.
- Performance:Your performance evaluations can influence your pay increases. Outstanding performance can lead to promotions or accelerated step increases, while poor performance may result in a delay in step increases.
- Location:Locality pay adjustments are based on the cost of living in your location. Employees in higher-cost areas receive larger adjustments.
- Economic Conditions:Economic conditions can also influence pay adjustments. During periods of high inflation, salary increases may be larger to offset the rising cost of living.
- Government Funding:Pay adjustments are ultimately dependent on government funding. Budget constraints can limit the amount of pay increases that can be awarded.
Impact of Pay Adjustments on Salary
The following table compares the effects of different pay adjustments on an employee’s salary:
| Pay Adjustment | Effect on Salary |
|---|---|
| Step Increase | Increases salary based on time in service and performance. |
| Locality Pay Adjustment | Increases salary based on cost of living in the employee’s location. |
Utilizing the Calculator for Career Planning
The GS Pay Calculator is not just a tool for understanding your current salary; it’s a powerful resource for making informed career decisions. By leveraging its capabilities, you can explore different career paths, estimate potential salary growth, and compare job opportunities to make strategic choices for your future.
Estimating Potential Salary Growth
Understanding potential salary growth is crucial for long-term career planning. The GS Pay Calculator can help you estimate this growth by allowing you to input different factors, such as your current grade and step, years of experience, and anticipated promotions.
For instance, let’s say you’re a GS-7 with 5 years of experience. You can use the calculator to see what your potential salary could be if you were to get promoted to a GS-9 after 3 years, assuming a standard step increase.
This information can help you set realistic salary goals and track your progress toward achieving them.
Comparing Different Job Opportunities
The GS Pay Calculator can be a valuable tool for comparing different job opportunities. By inputting the grade and step for each position, you can see the potential salary range and determine which offer aligns best with your financial goals.
For example, you might be offered two positions: one as a GS-9, step 5, and another as a GS-10, step 1. Using the calculator, you can see that the GS-10 position offers a higher starting salary, even though it’s a lower step.
This allows you to make informed decisions based on not only job responsibilities and career growth potential but also financial compensation.
Mastering the GS Pay Calculator is essential for IT professionals seeking to understand their potential earnings within the federal government. The calculator utilizes the complex GS Pay Scale, which is updated annually. For a detailed breakdown of the 2024 GS Pay Scale specifically tailored for IT professionals, refer to this comprehensive guide: Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals.
By familiarizing yourself with the GS Pay Scale and utilizing the calculator effectively, you can make informed decisions regarding your career trajectory and financial planning within the federal IT sector.
Resources and Additional Information
This section provides a comprehensive list of resources and websites that can offer further insights into GS pay and the GS Pay Calculator. These resources can be invaluable for understanding the nuances of the GS pay system and its implications for your career.
Official Government Resources, Mastering the GS Pay Calculator: Tips and Tricks
Government websites are the most reliable sources for information on GS pay. They provide official guidelines, regulations, and updates on the system.
- Office of Personnel Management (OPM):The OPM is the primary agency responsible for administering the federal government’s pay system. Their website provides comprehensive information on GS pay, including pay scales, locality adjustments, and other relevant information.
- Federal Pay Schedules:The Federal Pay Schedules are official documents published by the OPM that Artikel the pay rates for each GS grade and step. These documents are essential for understanding the specific pay rates associated with your GS position.
- United States Government Accountability Office (GAO):The GAO provides independent and nonpartisan oversight of the federal government, including its pay system. Their website offers reports and analyses on GS pay and related issues.
Other Useful Resources
Beyond government websites, other resources can provide valuable information on GS pay and career planning.
- Federal Employee Education and Assistance Fund (FEEA):The FEEA is a non-profit organization that provides resources and support to federal employees. Their website offers information on GS pay, benefits, and career development.
- Federal Times:This online publication provides news and information on the federal government, including articles on GS pay, pay raises, and other relevant issues.
- Federal Career Experts:Many websites and blogs offer advice and insights on navigating federal careers, including information on GS pay and the GS Pay Calculator.
Table of Top Resources
The following table summarizes the top three resources for GS pay information, highlighting their key strengths:
| Resource | Key Strengths |
|---|---|
| Office of Personnel Management (OPM) | Official source for GS pay information, comprehensive guidelines, pay scales, and updates. |
| Federal Pay Schedules | Detailed information on pay rates for each GS grade and step, published by the OPM. |
| United States Government Accountability Office (GAO) | Independent oversight of the federal pay system, reports and analyses on GS pay and related issues. |
Epilogue: Mastering The GS Pay Calculator: Tips And Tricks
So, whether you’re a seasoned government employee or a fresh-faced newcomer, embracing the GS Pay Calculator is like unlocking a treasure chest of financial insights. With a little know-how and a dash of confidence, you’ll be a master of your own compensation, ready to take on any career challenge that comes your way.
Now go forth, dear reader, and conquer the world of government pay with a smile and a calculator in hand!


