GS Pay and Incentive Pay: Bonuses and Awards, a vital part of the federal government’s compensation system, offers a nuanced approach to rewarding and motivating its workforce. This system, encompassing both base salary and performance-based incentives, aims to attract and retain talented individuals while fostering a culture of excellence.
Understanding the intricacies of GS Pay and Incentive Pay is crucial for both current and prospective federal employees. This system encompasses a complex web of factors, including base salary, performance evaluations, and eligibility for various bonus programs. It’s a system that rewards dedication, achievement, and the pursuit of continuous improvement.
By delving into the details of GS Pay and Incentive Pay, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the mechanisms that drive success within the federal workforce.
Understanding GS Pay and Incentive Pay
The federal government employs a complex system for compensating its workforce, encompassing both base salaries and performance-based incentives. This system ensures fair compensation while recognizing exceptional contributions.
General Schedule (GS) Pay
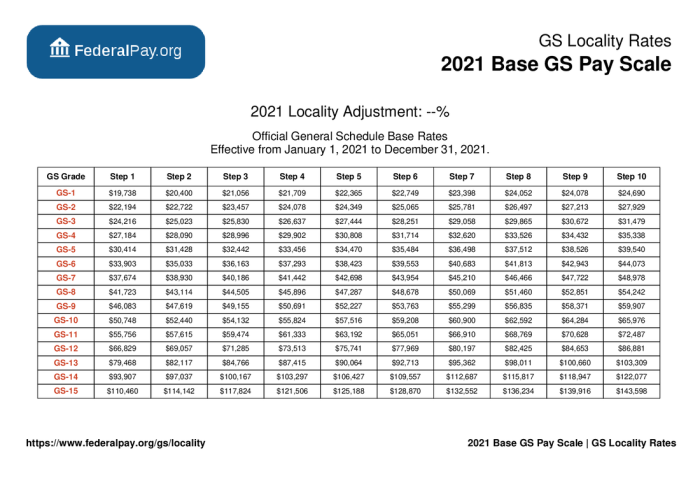
The General Schedule (GS) pay system is the foundation for federal employee compensation. It establishes a standardized pay scale based on grade levels and steps within each grade. The GS pay system is designed to ensure that employees are compensated fairly based on their experience, education, and the complexity of their job responsibilities.
- Grade Levels:GS grades range from GS-1 to GS-15, with higher grades indicating greater responsibility and expertise. Each grade has multiple steps, representing incremental increases in pay within that grade.
- Step Increases:Employees progress through the steps within their grade based on their performance and length of service. This allows for gradual salary increases as employees gain experience and demonstrate their value.
- Locality Pay Adjustments:The GS pay system incorporates locality pay adjustments to account for regional differences in cost of living. This ensures that federal employees are compensated competitively across the country.
Incentive Pay
Incentive pay, including bonuses and awards, serves as a mechanism to recognize and reward exceptional performance and contributions beyond the standard GS pay system. It provides an additional layer of compensation to motivate employees and encourage high levels of productivity.
- Performance-Based Bonuses:These bonuses are awarded to employees who consistently exceed performance expectations. The criteria for awarding performance bonuses are typically tied to specific performance goals or metrics.
- Awards:Awards are given to employees who make significant contributions to the agency or the government as a whole. These awards can range from cash awards to recognition plaques or certificates.
Comparing GS Pay and Incentive Pay
- Basis of Compensation:GS pay is based on an employee’s grade level, step, and locality pay adjustment, while incentive pay is based on individual performance and contributions.
- Frequency:GS pay is typically received on a regular basis (e.g., bi-weekly), while incentive pay is awarded periodically based on performance reviews or specific achievements.
- Purpose:GS pay is designed to ensure fair and competitive compensation for all federal employees, while incentive pay aims to recognize and reward exceptional performance and contributions.
Types of Incentive Pay
Incentive pay, also known as performance-based pay, is a system where federal employees receive additional compensation for exceeding performance expectations or achieving specific goals. This type of pay is designed to motivate employees, enhance productivity, and reward exceptional contributions.
Types of Incentive Pay
The federal government offers a variety of incentive pay programs to recognize and reward exceptional performance. These programs can be categorized based on their purpose and eligibility criteria.
- Performance-Based Awards: These awards are given to employees who demonstrate exceptional performance, exceeding established standards and contributing significantly to organizational success. They are typically awarded on an individual basis, based on specific performance criteria and evaluations. Examples include:
- Cash Awards: These are lump-sum payments given to employees who have achieved outstanding performance, exceeding expectations in their roles.
They are often used to recognize significant accomplishments, innovative solutions, or exceptional contributions to organizational goals.
- Quality Step Increases (QSI): These are non-performance-based awards granted to employees who consistently demonstrate high levels of performance over a sustained period, typically exceeding performance expectations for a specified duration. They are awarded based on a structured performance evaluation system, with specific criteria for eligibility.
- Performance Awards: These awards recognize employees who have consistently demonstrated exceptional performance, significantly exceeding established standards and making significant contributions to organizational success. They are awarded based on a comprehensive performance evaluation process, considering factors such as individual achievements, team contributions, and overall impact on organizational goals.
- Cash Awards: These are lump-sum payments given to employees who have achieved outstanding performance, exceeding expectations in their roles.
- Special Awards: These awards are given to employees who have made significant contributions to the government, often exceeding the scope of their regular duties or going above and beyond expectations. They are typically awarded for extraordinary achievements, exceptional leadership, or significant contributions to public service.
So, you wanna know about GS Pay and those sweet bonuses? Let’s talk about it. Knowing the GS Pay Scale can be your secret weapon for landing those extra bucks. Check out Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrative Assistants to get the lowdown.
Understanding how it works can help you snag that sweet incentive pay, and you know what that means? More cash for your next shopping spree!
Examples include:
- Presidential Rank Awards: These awards are the highest recognition bestowed upon federal employees, acknowledging exceptional contributions to the government. They are awarded by the President of the United States to individuals who have demonstrated outstanding performance, leadership, and commitment to public service.
- Distinguished Executive Awards: These awards recognize exceptional leadership and contributions by senior executives in the federal government. They are awarded to individuals who have demonstrated outstanding leadership, strategic vision, and significant contributions to the success of their agencies.
- Meritorious Executive Awards: These awards recognize exceptional performance and contributions by senior executives in the federal government. They are awarded to individuals who have demonstrated outstanding leadership, strategic vision, and significant contributions to the success of their agencies.
- Incentive Pay Programs: These programs offer additional compensation to employees who work in specific occupations or perform specific duties that require specialized skills, knowledge, or expertise. They are designed to attract and retain qualified personnel in critical roles. Examples include:
- Law Enforcement Availability Pay: This pay is provided to law enforcement officers who are required to be available for duty on a 24/7 basis, including nights, weekends, and holidays.
It is designed to compensate officers for the inconvenience and sacrifices associated with their demanding work schedules.
- Recruitment and Retention Incentive Pay: This pay is offered to employees in specific occupations or locations where it is difficult to recruit and retain qualified personnel. It is designed to make these positions more attractive and competitive, ensuring the government can fill critical roles.
- Critical Skills Pay: This pay is awarded to employees who possess specialized skills, knowledge, or expertise that are essential to the government’s mission. It is designed to recognize and reward employees who possess rare and valuable skills, ensuring the government can retain these individuals.
- Law Enforcement Availability Pay: This pay is provided to law enforcement officers who are required to be available for duty on a 24/7 basis, including nights, weekends, and holidays.
Purpose and Typical Award Amounts
The following table provides a summary of the different types of incentive pay, their purpose, and typical award amounts.
| Type of Incentive Pay | Purpose | Typical Award Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Performance-Based Awards | Recognize exceptional performance and contributions | Varies depending on performance level and agency policies |
| Special Awards | Recognize significant contributions and achievements | Varies depending on the level of achievement and agency policies |
| Incentive Pay Programs | Attract and retain qualified personnel in critical roles | Varies depending on the specific program and agency policies |
Eligibility and Award Criteria
Incentive pay programs are designed to motivate employees and reward exceptional performance. To ensure fairness and effectiveness, clear eligibility and award criteria are established. These criteria Artikel the qualifications necessary for receiving incentive pay and the factors considered in determining the amount and frequency of bonus awards.
General Eligibility Requirements
To be eligible for incentive pay, employees typically need to meet specific criteria related to their job role, performance, and tenure.
- Job Role:Incentive pay programs often target specific job roles or departments that are critical to the organization’s success. Employees in these roles may be eligible for bonuses or awards based on their individual or team performance.
- Performance:Employees must consistently demonstrate a high level of performance in their roles. This may include exceeding expectations, meeting or exceeding performance goals, or contributing to the organization’s overall success.
- Tenure:Some incentive pay programs may have minimum tenure requirements, meaning employees must have been with the organization for a certain period before becoming eligible. This helps ensure that employees have a sufficient understanding of the company’s goals and values.
Award Criteria
The amount and frequency of bonus awards are determined based on various factors, including individual and team performance, organizational profitability, and the specific incentive pay program guidelines.
- Performance Metrics:Organizations typically use specific performance metrics to measure employee performance and determine bonus eligibility. These metrics can include sales figures, customer satisfaction ratings, productivity levels, or project completion rates.
- Achievement Levels:Incentive pay programs often have different tiers or levels of awards based on achievement levels. For example, employees who exceed expectations or achieve significant milestones may receive larger bonuses than those who meet minimum performance standards.
- Organizational Performance:The overall financial performance of the organization can also influence bonus awards. If the company experiences significant growth or profitability, employees may receive larger bonuses or more frequent awards.
Examples of Performance Metrics
- Sales Revenue:For sales professionals, exceeding sales targets or generating a specific amount of revenue can qualify for incentive pay.
- Customer Satisfaction:Employees who consistently receive positive customer feedback or achieve high customer satisfaction scores may be eligible for bonuses.
- Productivity:Employees who increase their output, improve efficiency, or reduce waste can be rewarded with incentive pay.
- Project Completion:Employees who successfully complete projects on time and within budget can receive bonuses based on the complexity and importance of the project.
Impact of Incentive Pay on Employee Motivation
Incentive pay, a form of compensation that rewards employees for achieving specific goals or exceeding performance expectations, has been a popular strategy for motivating employees and driving business results. However, the effectiveness of incentive pay in boosting employee motivation and performance is a subject of ongoing debate.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Incentive Pay
Incentive pay can be a powerful tool for enhancing employee motivation and performance. It can encourage employees to work harder, achieve goals, and improve their skills. However, it’s important to acknowledge that incentive pay can also have drawbacks.
- Increased Productivity and Performance: Incentive pay can motivate employees to strive for higher levels of productivity and performance, leading to improved overall business results. For instance, a sales team incentivized by commission-based pay might be more likely to close deals and increase revenue.
- Enhanced Focus on Goals: Incentive pay programs often focus on specific goals and objectives, aligning employee efforts with the company’s strategic priorities. This can lead to a more targeted and efficient approach to work.
- Improved Employee Engagement: When employees feel that their contributions are recognized and rewarded, they are more likely to feel engaged in their work and committed to the organization’s success.
- Potential for Short-Term Focus: Incentive pay programs can sometimes encourage employees to prioritize short-term gains over long-term objectives, potentially leading to a neglect of important tasks or strategic initiatives.
- Unintended Consequences: Incentive pay programs can sometimes lead to unintended consequences, such as unhealthy competition among employees, a focus on individual performance at the expense of teamwork, or a decline in intrinsic motivation.
- Potential for Reduced Collaboration: Incentive pay systems that reward individual performance can sometimes discourage collaboration and teamwork, as employees may focus on maximizing their own rewards rather than working together to achieve common goals.
Perspectives on the Effectiveness of Incentive Pay
Different perspectives exist on the effectiveness of incentive pay in driving employee engagement.
- Behaviorist Perspective: This perspective emphasizes the importance of external rewards in motivating behavior. Proponents argue that incentive pay can effectively shape employee behavior and encourage desired actions.
- Cognitive Perspective: This perspective highlights the role of cognitive factors, such as perceptions of fairness and equity, in influencing employee motivation. It suggests that incentive pay programs should be designed in a way that is perceived as fair and equitable by employees to be effective.
- Social-Cognitive Perspective: This perspective emphasizes the importance of social and cognitive factors in shaping employee motivation. It suggests that incentive pay programs can be more effective when they are combined with other motivational strategies, such as providing opportunities for growth and development, fostering a positive work environment, and recognizing employee contributions.
Factors Influencing Incentive Pay Effectiveness, GS Pay and Incentive Pay: Bonuses and Awards
Several factors can influence the effectiveness of incentive pay programs.
So, you’re thinking about that sweet GS Pay and those juicy incentive bonuses, right? Well, let’s be real, knowing the ins and outs of the GS Pay Scale is key to maximizing your earning potential. Check out this guide, GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources: A Comprehensive Guide , to get the lowdown on what you can expect.
Armed with this knowledge, you’ll be able to strategize and snag those sweet bonuses like a pro!
- Clarity of Goals and Objectives: Incentive pay programs should be designed with clear and measurable goals and objectives that are aligned with the organization’s strategic priorities. This ensures that employees understand what they need to do to earn rewards and that their efforts are directed towards achieving desired outcomes.
- Fairness and Equity: Incentive pay programs should be perceived as fair and equitable by employees. This means that the criteria for earning rewards should be clear, transparent, and consistently applied. Employees should feel that they have a fair chance of earning rewards based on their performance.
- Employee Involvement: Involving employees in the design and implementation of incentive pay programs can help ensure that the programs are relevant and motivating. Employees are more likely to buy into programs that they feel have been developed with their input and that address their needs and concerns.
So, you’re thinking about GS Pay and Incentive Pay, huh? Bonuses and awards are cool, but you gotta know your worth! Check out Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals to get the lowdown on how the system works.
Once you’re in the know, you can hustle for those sweet bonuses and awards!
- Communication and Feedback: Open and frequent communication about the incentive pay program is essential. Employees should be informed about the program’s goals, criteria, and progress. Regular feedback on performance and progress towards goals can help employees stay motivated and focused.
- Cultural Fit: The effectiveness of incentive pay programs can also depend on the organization’s culture. In organizations with a strong performance-driven culture, incentive pay programs can be a powerful tool for motivating employees. However, in organizations with a more collaborative or team-oriented culture, incentive pay programs may need to be designed in a way that encourages teamwork and collaboration.
Best Practices for Incentive Pay Programs
Designing and implementing effective incentive pay programs is crucial for attracting and retaining top talent in the public sector. By aligning individual performance with organizational goals, incentive pay can boost employee motivation, enhance productivity, and improve overall service delivery.
Designing Incentive Pay Programs
Designing an effective incentive pay program requires careful consideration of several factors, including the specific goals and objectives of the program, the target audience, and the available resources.
- Clearly Define Program Goals and Objectives:Establishing clear and measurable goals and objectives for the program is essential. This ensures that the incentive pay is aligned with the organization’s strategic priorities and that employees understand what they need to achieve to receive rewards. For example, a program designed to improve customer service could set goals such as reducing wait times or increasing customer satisfaction ratings.
- Target the Right Audience:It’s important to identify the specific group of employees who will be eligible for the incentive pay. This could be based on job roles, performance levels, or other criteria. Targeting the right audience ensures that the program is relevant and motivating to the employees who are most likely to contribute to achieving the program’s goals.
- Develop Measurable Performance Indicators:Performance indicators should be quantifiable and directly related to the program’s goals. This allows for objective evaluation of employee performance and ensures that the incentive pay is awarded fairly. Examples of performance indicators include sales targets, customer satisfaction scores, and productivity metrics.
- Set Realistic and Achievable Targets:Targets should be challenging but attainable. Setting unrealistic targets can lead to demotivation and a perception that the program is unfair. Conversely, targets that are too easy will not provide sufficient incentive for employees to strive for excellence.
- Communicate Clearly and Regularly:Effective communication is essential for ensuring that employees understand the program’s rules, eligibility criteria, and performance expectations. Regular communication can help maintain employee engagement and address any concerns or questions.
- Use a Variety of Incentive Pay Options:Offering a range of incentive pay options, such as cash bonuses, performance-based raises, and recognition awards, can appeal to a wider range of employees. This can also provide flexibility in rewarding employees for different types of contributions.
Ensuring Fairness, Transparency, and Accountability
Fairness, transparency, and accountability are crucial for maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of an incentive pay program.
- Establish Clear and Transparent Award Criteria:The criteria for awarding incentive pay should be clearly defined and communicated to all employees. This ensures that everyone understands the basis for receiving rewards and that the process is fair and equitable.
- Use Objective Performance Measures:Using objective performance measures helps ensure that incentive pay is awarded based on actual performance rather than subjective opinions. This reduces the risk of bias and promotes a culture of fairness.
- Provide Regular Feedback and Performance Reviews:Providing employees with regular feedback and performance reviews can help them understand their progress towards achieving performance targets and identify areas for improvement. This also provides an opportunity to address any concerns or questions about the incentive pay program.
- Establish an Appeal Process:An appeal process allows employees to challenge decisions regarding incentive pay if they believe that the process was unfair or that the criteria were not applied correctly. This provides a mechanism for resolving disputes and ensures that the program is fair and accountable.
Successful Incentive Pay Programs
Several government agencies have implemented successful incentive pay programs that have contributed to improved performance and increased employee motivation.
- The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA):The VA’s Performance-Based Pay program has been credited with improving employee performance and reducing wait times for veterans seeking healthcare services. The program rewards employees for achieving specific performance goals, such as reducing wait times or improving patient satisfaction ratings.
- The U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS):DHS has implemented a variety of incentive pay programs, including performance-based bonuses and recognition awards, to reward employees for outstanding contributions to national security. These programs have helped to attract and retain top talent in the critical field of homeland security.
- The U.S. Department of Education (ED):The ED has implemented a program that provides bonuses to teachers who achieve high student performance results. The program has been credited with improving student outcomes and motivating teachers to strive for excellence.
Future Trends in Incentive Pay: GS Pay And Incentive Pay: Bonuses And Awards
The government’s incentive pay programs are constantly evolving to adapt to changing economic conditions, technological advancements, and evolving workforce needs. These programs are designed to attract and retain talented individuals, motivate high performance, and ensure the efficient delivery of public services.
Here’s a look at some of the future trends shaping the landscape of incentive pay in the public sector.
Performance-Based Pay
Performance-based pay is a key trend that’s likely to gain even greater prominence in the future. This approach emphasizes rewarding employees based on their individual or team contributions, rather than solely on seniority or time served. It aligns incentives with organizational goals and encourages a culture of achievement.
Epilogue
GS Pay and Incentive Pay, with its blend of base salary and performance-based bonuses, plays a pivotal role in shaping the federal workforce. It’s a system that encourages dedication, rewards achievement, and motivates employees to strive for excellence. By understanding the intricacies of this system, individuals can navigate the path to career advancement within the federal government, unlocking the potential for both personal and professional growth.


