GS Pay and Overtime: Rules and Exceptions takes center stage, navigating the complex world of federal government employee compensation. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate details of GS pay, overtime eligibility, and the nuances that govern these crucial aspects of federal employment.
Whether you are a seasoned GS employee seeking clarity on overtime regulations or a new recruit eager to understand your compensation structure, this exploration will equip you with the knowledge you need to confidently navigate the intricacies of GS pay and overtime.
Understanding the fundamental principles of GS pay, including grade, step, and locality pay, forms the bedrock of this exploration. We will then delve into the different types of overtime available to GS employees, their eligibility criteria, and the intricate calculations involved.
This journey will also shed light on the various exceptions to overtime rules, including the administrative, professional, and executive exemptions, providing practical examples to illustrate their application.
Understanding GS Pay and Overtime
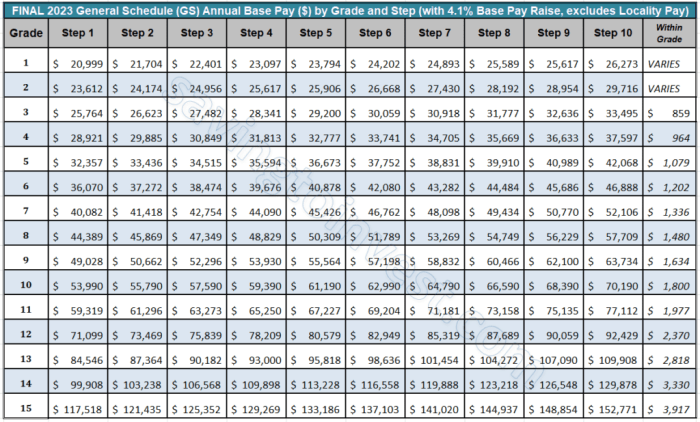
The General Schedule (GS) pay system is a federal government pay system that sets salaries for most civilian employees. It differs from other pay systems in its structured approach to determining pay based on grade, step, and locality pay.
GS Pay System Basics
The GS pay system is based on a hierarchical structure that categorizes positions according to their complexity, responsibility, and knowledge requirements. Each grade represents a different level of responsibility and expertise. Within each grade, there are steps that represent incremental increases in pay based on years of service and performance.
GS pay is determined by a combination of factors, including:
- Grade:Indicates the level of responsibility and expertise required for the position.
- Step:Represents incremental increases in pay based on years of service and performance within a specific grade.
- Locality Pay:Adjusts GS pay based on the cost of living in different geographic areas.
Overtime for GS Employees
GS employees are eligible for overtime pay for hours worked beyond their regular work schedule. The type of overtime available depends on the employee’s position and work schedule.
The two primary types of overtime for GS employees are:
- Standard Overtime:Paid at a rate of 1.5 times the employee’s regular hourly rate for hours worked beyond 8 hours in a workday or 40 hours in a workweek.
- Premium Pay:Paid at a rate of 2 times the employee’s regular hourly rate for certain types of work, such as working on holidays or weekends.
Overtime Eligibility and Calculation
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) sets the rules for overtime pay for most U.S. workers, including those employed by the federal government. This section will discuss the FLSA regulations applicable to GS employees and how they affect overtime eligibility.
Navigating the labyrinthine world of GS Pay and overtime rules can be a frustrating experience, especially when faced with seemingly arbitrary exceptions. Understanding the intricacies of the GS Pay Scale, including overtime regulations, is crucial for any HR professional, and a resource like GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources: A Comprehensive Guide can be a valuable tool.
By mastering the complexities of the GS Pay system, HR professionals can ensure fair compensation and compliance, ultimately fostering a more stable and productive workforce.
Overtime Eligibility for GS Employees
The FLSA requires employers to pay overtime to eligible employees who work more than 40 hours in a workweek. GS employees are generally eligible for overtime pay, but there are some exceptions and specific circumstances that determine eligibility. Here’s a breakdown of key factors:
Work exceeding 40 hours per week
- GS employees are generally eligible for overtime pay for any hours worked over 40 in a workweek.
- The workweek is a fixed, seven-day period, not necessarily Monday through Sunday.
- Overtime is calculated on a weekly basis, not on a daily or bi-weekly basis.
Work on weekends and holidays
- Work performed on weekends and holidays is considered regular work time and counts towards the 40-hour threshold for overtime eligibility.
- If a GS employee works more than 40 hours in a workweek that includes a weekend or holiday, they are eligible for overtime pay for the hours worked over 40.
Work performed under certain conditions
- GS employees may be eligible for overtime pay for work performed under certain conditions, such as work performed during a “compensable standby” period or work performed on a “regularly scheduled” day off.
- The specific conditions under which overtime pay is required for these situations are Artikeld in the FLSA and may vary depending on the specific circumstances.
Calculating Overtime Pay
Overtime pay for GS employees is calculated at a rate of one and a half times the employee’s regular rate of pay. This means that for every hour worked over 40 in a workweek, the employee is paid 1.5 times their regular hourly rate.
Calculating the Overtime Rate
- To calculate the overtime rate, multiply the employee’s regular hourly rate by 1.5.
- For example, if an employee’s regular hourly rate is $20, their overtime rate would be $30 (20 x 1.5).
Calculating Overtime Pay
- To calculate overtime pay, multiply the number of overtime hours worked by the overtime rate.
- For example, if an employee works 45 hours in a workweek, they would be eligible for 5 hours of overtime pay (45 hours worked – 40 hours regular work = 5 hours overtime).
- If the employee’s overtime rate is $30, their total overtime pay for the week would be $150 (5 hours overtime x $30 overtime rate).
Additional Premiums
- In some cases, GS employees may be eligible for additional premiums for overtime work, such as night differential pay or hazardous duty pay.
- These premiums are added to the employee’s regular pay and overtime pay.
Exceptions to Overtime Rules
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) mandates overtime pay for most employees who work more than 40 hours in a workweek. However, there are certain exemptions to this rule, which can be applied to GS employees based on their job duties and responsibilities.
These exemptions are designed to exclude certain types of employees from overtime pay requirements, typically those who hold positions of significant responsibility or whose work is considered to be highly specialized.
Administrative Exemption
The administrative exemption applies to employees who are primarily engaged in office or non-manual work directly related to the management or general business operations of the employer or its customers. To qualify for this exemption, the employee must meet all of the following criteria:
- They must be compensated on a salary basis at a rate not less than $684 per week.
- Their primary duty must be the performance of office or non-manual work directly related to the management or general business operations of the employer or its customers.
- Their primary duty must include the exercise of discretion and independent judgment with respect to matters of significance.
An example of an employee who might qualify for the administrative exemption is a manager responsible for overseeing a team of employees, developing budgets, and making decisions about resource allocation.
Professional Exemption
The professional exemption applies to employees who are primarily engaged in work requiring advanced knowledge, in a field of science or learning, customarily acquired by a prolonged course of specialized intellectual instruction. This exemption applies to specific professions, including teachers, lawyers, doctors, and accountants.
To qualify for this exemption, the employee must meet all of the following criteria:
- They must be compensated on a salary basis at a rate not less than $684 per week.
- Their primary duty must be the performance of work requiring advanced knowledge, in a field of science or learning, customarily acquired by a prolonged course of specialized intellectual instruction.
- Their primary duty must involve the consistent exercise of discretion and judgment.
An example of an employee who might qualify for the professional exemption is a certified public accountant who performs audits and prepares financial statements.
Executive Exemption
The executive exemption applies to employees who are primarily engaged in managing the enterprise, or a customarily recognized department or subdivision thereof. To qualify for this exemption, the employee must meet all of the following criteria:
- They must be compensated on a salary basis at a rate not less than $684 per week.
- Their primary duty must be managing the enterprise, or a customarily recognized department or subdivision thereof.
- Their primary duty must include directing the work of two or more other employees.
- Their primary duty must include the authority to hire or fire other employees, or their suggestions and recommendations as to the hiring, firing, advancement, promotion, or any other change of status of other employees must be given particular weight.
An example of an employee who might qualify for the executive exemption is a department head who oversees a team of employees, sets goals, and makes decisions about staffing and budgets.
Common Overtime Issues and Resolutions
Navigating overtime pay in the federal government can sometimes present challenges. GS employees may encounter situations where they believe they are owed overtime but haven’t received it, or they might have questions about their overtime eligibility. This section will explore some common issues and provide guidance on how to address them.
Disputes Over Overtime Eligibility
It’s crucial to understand the criteria for overtime eligibility. If you believe you are eligible for overtime but haven’t received it, it’s important to gather information and address the situation.
- Review your job description and the FLSA (Fair Labor Standards Act) regulations to confirm if your position is eligible for overtime.
- Keep accurate records of your work hours, including any overtime worked.
- If you believe you are eligible for overtime, discuss your concerns with your supervisor or HR department.
Incorrect Overtime Calculations
Errors in overtime calculations can happen, leading to underpayment.
- Carefully review your pay stubs to ensure your overtime hours are accurately reflected.
- If you notice any discrepancies, contact your HR department or payroll office to investigate and correct the error.
Missed Overtime Payments
Sometimes, overtime payments might be missed or delayed.
The labyrinthine world of GS Pay and Overtime: Rules and Exceptions can leave even the most seasoned administrative assistant feeling lost. While the system boasts a complex web of regulations, it’s crucial to understand how your pay and overtime are calculated, especially with the upcoming changes in the GS Pay Scale for 2024.
Navigating this system can be daunting, but resources like Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrative Assistants can provide valuable insights. Understanding the nuances of GS Pay and Overtime is not just about ensuring you’re being compensated fairly, but also about advocating for yourself and ensuring you receive the benefits you’re entitled to.
- If you are owed overtime pay and it hasn’t been received by the expected date, contact your HR department or payroll office to inquire about the status of your payment.
Resolving Overtime Issues, GS Pay and Overtime: Rules and Exceptions
Several avenues exist to resolve overtime issues.
- Filing a Grievance:If you have exhausted all other avenues and believe your overtime pay is being unfairly withheld, you can file a formal grievance through your agency’s grievance process.
- Contacting the Office of Personnel Management (OPM):OPM sets the standards for federal employee pay and benefits, including overtime. If you believe your agency is not following OPM guidelines, you can contact OPM for assistance.
- Seeking Legal Advice:In some cases, seeking legal advice from an employment lawyer may be necessary to protect your rights.
Real-World Scenarios
Scenario 1:
A GS-9 employee working as a paralegal is required to work late on a regular basis to meet deadlines. The employee is not paid overtime. In this case, the employee should first consult their job description to confirm their overtime eligibility.
The labyrinthine rules governing GS pay and overtime often leave federal IT professionals feeling like they’re navigating a bureaucratic minefield. While the government claims to offer a fair system, the reality is that exceptions and loopholes abound, leaving many underpaid and overworked.
For those seeking clarity in this complex system, Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals can provide a starting point, though even the most detailed guides can’t account for the ever-shifting sands of federal bureaucracy.
Ultimately, the struggle for fair compensation and reasonable work hours remains a constant battle for those on the front lines of government IT.
If they are eligible, they should raise the issue with their supervisor and HR department. If the issue persists, they can file a grievance or contact OPM for assistance.
Scenario 2:
A GS-12 employee working as a budget analyst receives a pay stub with an incorrect overtime calculation. The employee should review their time records and compare them to the pay stub. If the calculation is incorrect, they should contact the payroll office to rectify the error.
Impact of Overtime on GS Pay and Benefits
Overtime work can significantly impact GS employees’ overall compensation and well-being. Understanding how overtime affects pay, benefits, and work-life balance is crucial for navigating this aspect of federal employment.
Impact on Total Compensation
Overtime pay is calculated at time-and-a-half the employee’s regular hourly rate for hours worked exceeding 40 in a workweek. This extra compensation can boost GS employees’ total earnings, contributing to their overall financial well-being. However, it’s important to note that overtime pay doesn’t always translate to a proportional increase in benefits.
- Base Pay:Overtime pay directly impacts total earnings, increasing the overall amount received for a given pay period. This can be particularly beneficial for employees who consistently work overtime, leading to a higher annual income.
- Bonuses:Overtime work may not always directly impact bonuses, which are typically based on performance, merit, or other criteria. While overtime pay contributes to higher overall earnings, it may not necessarily guarantee a larger bonus.
- Benefits:Some benefits, such as health insurance premiums, are based on salary, so overtime pay may lead to higher premiums. Other benefits, such as retirement contributions, may not be affected by overtime pay.
Potential Implications for Work-Life Balance, Stress Levels, and Employee Morale
While overtime pay can provide financial benefits, excessive overtime can negatively impact work-life balance, stress levels, and employee morale.
- Work-Life Balance:Extended work hours due to overtime can significantly impact an employee’s ability to maintain a healthy work-life balance. It can lead to reduced time for personal commitments, family responsibilities, and leisure activities.
- Stress Levels:The demands of overtime work can contribute to increased stress levels, potentially leading to burnout, fatigue, and health issues.
- Employee Morale:Consistent overtime work can negatively impact employee morale. It can lead to feelings of exhaustion, resentment, and dissatisfaction, potentially affecting productivity and overall job satisfaction.
Strategies for Managing Overtime Work and Its Impact
GS employees can adopt various strategies to manage overtime work and mitigate its potential negative impact on their well-being.
- Open Communication:Maintaining open communication with supervisors regarding workload and overtime expectations is crucial. This allows for proactive discussion and potential adjustments to work schedules or task prioritization.
- Prioritization and Time Management:Effective time management and task prioritization can help manage workload and minimize the need for overtime.
- Self-Care:Prioritizing self-care activities, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and healthy eating, is essential for managing stress and maintaining well-being.
- Boundaries:Setting clear boundaries between work and personal life is crucial for preserving work-life balance.
- Seeking Support:Don’t hesitate to seek support from colleagues, supervisors, or employee assistance programs if feeling overwhelmed or struggling with the demands of overtime work.
Final Review: GS Pay And Overtime: Rules And Exceptions
As we conclude this exploration of GS Pay and Overtime: Rules and Exceptions, the importance of clarity and awareness shines through. Armed with this knowledge, GS employees can confidently navigate the intricacies of their compensation, ensuring fair treatment and understanding the nuances of overtime eligibility.
By proactively addressing common overtime issues and resolving disputes, employees can safeguard their rights and advocate for their well-being. Remember, this is not just about understanding rules, but about empowering yourself to navigate the complexities of federal employment with confidence and clarity.


