GS Pay and Remote Work: Trends and Challenges sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Imagine a world where your office is your couch, your commute is a trip to the coffee pot, and your boss is just a video call away.
This is the reality of remote work, and with it comes a whole new set of rules for how we get paid. We’re talking about GS Pay, the salary structure that’s trying to keep up with the changing times.
From navigating the complexities of location-based pay to the challenges of ensuring fairness in a virtual workplace, this journey is packed with twists and turns.
This article dives into the heart of GS Pay in the age of remote work, exploring the trends, challenges, and potential future of this ever-evolving landscape. We’ll dissect the factors that influence GS Pay, from the cost of living to the ever-present specter of bias.
And just when you think you’ve got it figured out, we’ll throw in some real-world examples of innovative GS Pay models that are rewriting the rules of the game. So buckle up, it’s going to be a wild ride!
GS Pay in the Remote Work Landscape
The rise of remote work has significantly impacted the traditional GS Pay structure, bringing about changes in how salaries are determined and managed. The shift to remote work has introduced new considerations and challenges for organizations in setting GS Pay for their employees.
Impact of Remote Work on GS Pay Structures
Remote work has led to a reevaluation of traditional GS Pay structures. The traditional model, which primarily considered factors such as location and cost of living, has been challenged by the geographically dispersed nature of remote workforces. Remote employees often reside in areas with lower cost of living, which can influence their salary expectations.
Factors Influencing GS Pay Levels in Remote Work
The factors that determine GS Pay levels have been influenced by the rise of remote work. These factors include:
- Cost of Living:While cost of living remains a factor, its impact is less pronounced in remote work scenarios. Companies often consider the cost of living in the employee’s location, but also take into account the company’s overall budget and the market rate for the specific role.
- Skills and Experience:The skills and experience required for a particular role continue to be a major factor in determining GS Pay. Remote work has led to a greater emphasis on specialized skills and the ability to work independently.
- Performance:Performance is a critical factor in determining GS Pay for both remote and in-office employees. Companies often implement performance-based compensation structures to reward high-performing individuals.
- Market Rates:Companies also consider market rates for similar roles to ensure they offer competitive salaries. The rise of remote work has increased competition for talent, leading to higher salaries in some cases.
- Company Culture and Values:Company culture and values can influence GS Pay. Companies that prioritize employee well-being and work-life balance may offer higher salaries to attract and retain top talent.
Comparison of GS Pay for Remote and In-Office Employees
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, GS Pay for remote and in-office employees can differ in several ways:
- Location Adjustments:Companies may adjust GS Pay for remote employees based on their location’s cost of living. This can involve offering a higher salary to compensate for a higher cost of living or a lower salary to reflect a lower cost of living.
The intersection of GS Pay and remote work presents both opportunities and challenges for HR professionals. As the landscape evolves, understanding the latest GS Pay scales is crucial for competitive recruitment and retention. For a comprehensive guide to the 2024 GS Pay Scale for Human Resources, check out GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources: A Comprehensive Guide.
This knowledge is vital to navigating the complexities of remote work compensation and ensuring a fair and equitable system for all employees.
- Remote Work Premium:Some companies offer a remote work premium, which is an additional amount of money paid to employees who work remotely. This premium can compensate for the additional expenses associated with working remotely, such as home office setup and internet costs.
The intersection of GS Pay and remote work presents unique challenges and opportunities. While remote work offers flexibility and potential for higher salaries, navigating the GS Pay Scale can be complex, especially for IT professionals. Understanding the intricacies of the GS Pay Scale and how it applies to remote work is crucial for maximizing your earning potential.
Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals provides valuable insights into the latest trends and strategies for success. This knowledge is essential for IT professionals seeking to leverage the advantages of remote work while maximizing their earning potential within the GS Pay structure.
- Flexibility and Work-Life Balance:Companies may offer higher salaries to attract and retain remote employees who value flexibility and work-life balance. This is particularly true for companies that offer flexible work arrangements and generous benefits packages.
Key Considerations for Setting GS Pay for Remote Workforces
Organizations need to consider several key factors when setting GS Pay for their remote workforces:
- Market Research:Conducting thorough market research is crucial to ensure GS Pay is competitive and reflects the current market rates for similar roles.
- Cost of Living Adjustments:Companies should consider cost of living adjustments for remote employees based on their location. This can involve using cost of living indices or conducting location-specific research.
- Remote Work Premium:Companies should consider offering a remote work premium to compensate for the additional expenses associated with working remotely. This premium can be a fixed amount or a percentage of the base salary.
- Performance-Based Compensation:Implementing performance-based compensation structures can ensure that high-performing remote employees are rewarded for their contributions.
- Flexibility and Benefits:Companies should offer flexible work arrangements and generous benefits packages to attract and retain top talent in a competitive remote work market.
Challenges of GS Pay in a Remote Work Environment
The transition to remote work has brought about significant changes in the way organizations manage compensation, particularly in the context of the General Schedule (GS) pay system. While remote work offers numerous benefits, it also presents unique challenges in ensuring equitable and transparent GS Pay practices.
Maintaining Equitable GS Pay Across Remote Teams
Ensuring equitable GS Pay across remote teams is a critical challenge. Traditional methods of evaluating performance and assigning GS Pay levels, often based on in-person interactions and proximity to supervisors, may not translate effectively to remote work environments. Remote employees may face challenges in demonstrating their contributions and receiving recognition for their work.
- Lack of Visibility:Remote employees may have limited opportunities to showcase their skills and achievements in a way that is easily visible to supervisors and colleagues. This can make it difficult for managers to accurately assess their performance and determine appropriate GS Pay levels.
- Different Performance Metrics:Remote work environments often require different performance metrics than traditional office settings. For example, remote employees may be evaluated on their output and results rather than on hours worked or physical presence. This can make it challenging to compare the performance of remote and in-person employees and ensure fair GS Pay.
- Remote Team Dynamics:Remote teams may experience challenges in fostering a sense of community and collaboration, which can impact performance and recognition. This can make it difficult to ensure that all team members receive equal opportunities for professional development and advancement, which are essential for GS Pay progression.
Potential for Bias in GS Pay Decisions for Remote Workers
There is a potential for bias in GS Pay decisions for remote workers, particularly if organizations do not have clear and transparent policies and procedures in place. This bias can manifest in various ways:
- Location-Based Bias:Organizations may unknowingly favor employees based on their physical location, even if they are performing the same work. For example, employees in metropolitan areas may be perceived as more valuable than those in rural areas, leading to discrepancies in GS Pay.
The rise of remote work has significantly impacted GS Pay, presenting both opportunities and challenges for administrative assistants. As more organizations embrace flexible work arrangements, understanding the intricacies of the GS Pay scale becomes crucial for navigating salary expectations and career advancement.
To demystify this complex system, consider exploring Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrative Assistants , which offers insights into pay grades, step increases, and other essential factors. By staying informed about the latest GS Pay trends and adapting to the evolving landscape of remote work, administrative assistants can position themselves for success in the modern workplace.
- Lack of Awareness of Remote Work Challenges:Managers may not fully understand the unique challenges faced by remote workers, leading to biased assessments of their performance and contributions. For example, managers may underestimate the demands of managing a home office or balancing work and family responsibilities.
- Unconscious Bias:Managers may unconsciously hold biases about remote workers, such as assuming that they are less productive or committed than in-person employees. These biases can influence GS Pay decisions, leading to unfair outcomes.
Trends in GS Pay and Remote Work: GS Pay And Remote Work: Trends And Challenges
The landscape of remote work is evolving rapidly, and with it, the methods of compensating remote employees are also undergoing significant transformations. GS Pay, a model that considers geographic location and cost of living, is gaining traction as a more equitable approach to remote worker compensation.
This section will explore current trends in GS Pay for remote workers, highlighting emerging models and the influence of location-based factors.
Current Trends in GS Pay for Remote Workers
The adoption of GS Pay models is increasing as companies recognize the need for a more equitable approach to compensating remote workers. This trend is driven by several factors, including:
- Growing remote workforce:The number of remote workers has surged in recent years, leading to a greater need for compensation models that address the unique challenges of remote work.
- Talent acquisition and retention:Companies are realizing that GS Pay can be a competitive advantage in attracting and retaining top talent in a global market.
- Equity and fairness:GS Pay models aim to ensure that remote workers are compensated fairly based on their location and the cost of living in their respective areas.
Emerging Trends in GS Pay Models for Remote Teams, GS Pay and Remote Work: Trends and Challenges
Beyond the traditional GS Pay approach, several innovative models are emerging specifically tailored for remote teams. These models aim to address the complexities of a geographically dispersed workforce:
- Location-based salary bands:This model establishes different salary bands based on specific locations or regions, taking into account cost of living and market conditions.
- Hybrid GS Pay:This model combines elements of traditional GS Pay with other compensation components, such as performance-based bonuses or equity grants, to provide a more comprehensive and flexible approach.
- Remote work stipends:Companies are offering stipends or allowances to remote workers to cover expenses related to remote work, such as home office equipment, internet access, or co-working space memberships.
Influence of Location and Cost of Living on GS Pay
The location and cost of living are key factors influencing GS Pay for remote workers. Companies typically consider the following:
- Cost of living index:This index measures the relative cost of goods and services in different locations, providing a benchmark for determining salary adjustments.
- Local market rates:Companies often research local market rates for comparable roles to ensure they are offering competitive salaries.
- Economic factors:Factors such as inflation, currency exchange rates, and local tax regulations can influence GS Pay adjustments.
Examples of Innovative GS Pay Models
Several companies have successfully implemented innovative GS Pay models for their remote teams. For example:
- Buffer:This remote-first company uses a location-based salary band system, ensuring that employees are compensated fairly based on their location and cost of living.
- GitLab:This remote-first company has implemented a hybrid GS Pay model that combines location-based salaries with performance-based bonuses and equity grants.
The Future of GS Pay and Remote Work
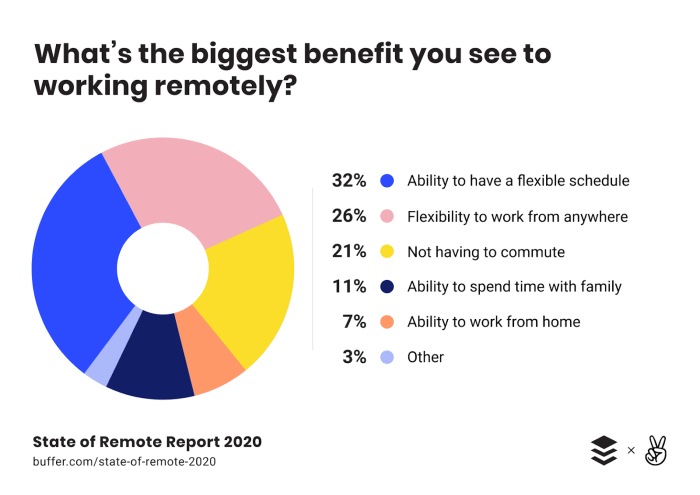
The landscape of work is rapidly evolving, with remote work becoming increasingly prevalent. This shift has significant implications for GS Pay structures, prompting a need to adapt and innovate to meet the demands of a distributed workforce. The future of GS Pay in a remote work environment is likely to be characterized by flexibility, technology-driven solutions, and a focus on employee well-being.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of GS Pay for remote workers.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered tools can automate tasks related to payroll processing, benefits administration, and performance management, leading to greater efficiency and accuracy. AI can also personalize compensation packages based on individual employee needs and preferences. For instance, AI-powered systems can analyze data on an employee’s skills, experience, and location to determine a fair and competitive salary.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent record-keeping for payroll and benefits, enhancing trust and accountability. It can also facilitate cross-border payments and simplify the administration of global workforces. Blockchain can be used to create a secure and transparent system for tracking employee contributions and benefits, ensuring that all parties have access to accurate information.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based platforms enable access to payroll and benefits information from anywhere, anytime, simplifying remote work management. Cloud computing also facilitates seamless integration with other HR systems, improving overall efficiency and reducing administrative burdens. For example, a company could use a cloud-based payroll system to allow employees to access their pay stubs and tax information online, regardless of their location.
Summary
As the lines between the office and home continue to blur, GS Pay is evolving right alongside it. We’ve seen the challenges, explored the trends, and glimpsed the future. The key takeaway? Flexibility and fairness are the cornerstones of successful GS Pay in a remote work environment.
So, whether you’re an employer trying to attract top talent or an employee seeking fair compensation, understanding the nuances of GS Pay in the remote work landscape is essential. It’s time to embrace the new normal, and with a little bit of creativity and collaboration, we can navigate the world of GS Pay and remote work with confidence, and maybe even a few laughs along the way.


