GS Pay Raises: What to Expect Annually – Wondering how much your paycheck might be boosted this year? The annual GS pay raise is a big deal for federal employees, and it’s always a hot topic of discussion.
We’ll dive into the factors that influence these raises, explore the projected percentage for the current fiscal year, and break down the impact on your salary. So, buckle up and get ready to learn how these raises affect your bottom line.
The GS pay raise system is complex, with factors like inflation, cost of living, and economic conditions all playing a role. We’ll explore the historical trends and analyze the key sources used to determine these projections. From understanding the different pay grades and salary ranges to comparing the raise structure across various occupations, we’ll cover everything you need to know about GS pay raises.
Understanding GS Pay Raises
The General Schedule (GS) pay scale is a standardized system used by the U.S. federal government to determine the salaries of its employees. GS pay raises are a crucial aspect of compensation for federal workers, impacting their financial well-being and career progression.
Understanding the factors that influence these raises and their historical trends can provide valuable insights for federal employees.
Factors Influencing GS Pay Raises
The annual GS pay raise is determined by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- The Federal Pay Act:This legislation sets the framework for determining GS pay raises, including the annual adjustment percentage. The act is reviewed and amended periodically to reflect economic conditions and ensure competitiveness with the private sector.
- Inflation:The rate of inflation, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), is a significant factor in determining GS pay raises. The goal is to ensure that employees’ purchasing power remains stable, even with rising prices.
- Cost of Living:The cost of living in different geographic areas varies, and the federal government often adjusts GS pay raises to account for these differences. This helps ensure that federal employees are fairly compensated regardless of their location.
- Economic Performance:The overall health of the economy, including factors like unemployment rates and GDP growth, can also influence GS pay raises. In times of economic prosperity, the government may be more likely to approve larger pay raises to attract and retain skilled employees.
- Budgetary Constraints:The federal government operates within a budget, and budgetary constraints can sometimes limit the size of GS pay raises. The government must balance the need to attract and retain qualified employees with the need to manage public funds effectively.
Historical Overview of GS Pay Raise Trends, GS Pay Raises: What to Expect Annually
Over the past five years, GS pay raises have generally reflected the overall economic environment.
Wondering how much that annual GS pay raise might be? It’s a question on everyone’s mind, especially those looking to climb the career ladder. But before you start planning that celebratory dinner, take a peek at Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrative Assistants to get a clear picture of your potential salary.
Understanding the GS pay scale can help you navigate your career trajectory and see those raises coming your way.
- 2018:GS pay raises were 2.1%, slightly exceeding the inflation rate at the time.
- 2019:GS pay raises were 2.0%, aligning with the inflation rate.
- 2020:GS pay raises were 3.1%, reflecting the economic uncertainty and rising inflation due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- 2021:GS pay raises were 2.7%, reflecting the ongoing economic recovery and inflation.
- 2022:GS pay raises were 4.6%, reflecting the highest inflation rate in decades.
Role of Inflation and Cost of Living
Inflation and cost of living play a crucial role in determining GS pay raises. The government aims to ensure that federal employees’ salaries keep pace with rising prices, maintaining their purchasing power.
“The Federal Pay Act directs that the annual adjustment for GS employees should be based on a comparison of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for Urban Wage Earners and Clerical Workers (CPI-W) for the most recent 12 months with the average CPI-W for the preceding 3 years.”
For example, if the CPI-W increases by 3% over the past year, the GS pay raise might be set at 3% to offset the inflation and ensure employees can maintain their standard of living.
Annual GS Pay Raise Expectations
The annual GS pay raise is a significant factor in the financial planning of federal employees. It directly impacts their take-home pay and overall compensation package. Understanding the projected raise for the current fiscal year and the factors influencing it is crucial for employees to make informed decisions about their finances.
Projected GS Pay Raise Percentage
The projected GS pay raise percentage for the current fiscal year is a crucial piece of information for federal employees. It allows them to anticipate their potential income increase and adjust their financial plans accordingly. The projected GS pay raise percentage for the current fiscal year (FY2024) is 2.7%.
This figure is based on a combination of factors, including the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the President’s budget proposal.
Wondering about those annual GS pay raises? They can be a bit of a mystery, but fret not! The good news is that there’s a handy guide for IT professionals navigating the GS Pay Scale in 2024, Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals.
This guide can help you understand those raises and make sure you’re getting the compensation you deserve. So, ditch the guesswork and dive into that guide – your future self will thank you!
Factors Influencing Projected GS Pay Raise
The projected GS pay raise is influenced by a variety of factors, including economic conditions, inflation, and government budget constraints. The primary factor considered in determining the GS pay raise is the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI is a measure of inflation that tracks changes in the cost of goods and services purchased by urban consumers.
The projected GS pay raise is typically aligned with the CPI to ensure that federal employees maintain their purchasing power in the face of rising prices. In addition to the CPI, other factors may influence the projected GS pay raise, including:
- President’s Budget Proposal:The President’s budget proposal Artikels the government’s spending priorities for the upcoming fiscal year. This proposal may include recommendations for GS pay raises that may differ from the CPI-based projections.
- Economic Conditions:The overall health of the economy can also influence the projected GS pay raise. In periods of economic growth, the government may be more likely to provide larger pay raises to attract and retain qualified employees. Conversely, during economic downturns, pay raises may be smaller or even frozen to reduce government spending.
- Government Budget Constraints:Government budget constraints can also play a role in determining the GS pay raise. If the government faces budget shortfalls, it may need to limit spending on pay raises to balance the budget.
Potential Impact of Economic Conditions
Economic conditions can significantly impact the projected GS pay raise. For example, during periods of high inflation, the projected GS pay raise may be higher to compensate for the increased cost of living. Conversely, during periods of economic recession, the projected GS pay raise may be lower or even frozen to reduce government spending.
It’s important to note that the projected GS pay raise is just an estimate. The actual pay raise may be different depending on the final budget negotiations and other factors.
GS Pay Raise Structure: GS Pay Raises: What To Expect Annually
The GS pay raise structure is a complex system that determines how much federal employees can expect to earn each year. Understanding this structure is crucial for both current and prospective federal employees, as it directly impacts their salary and career progression.The GS pay system is divided into 15 pay grades, with each grade representing a different level of experience and responsibility.
Within each grade, there are 10 steps, representing incremental salary increases based on time in service and performance. The salary range for each grade and step is determined by a combination of factors, including the employee’s location, occupation, and performance.
GS Pay Grades and Salary Ranges
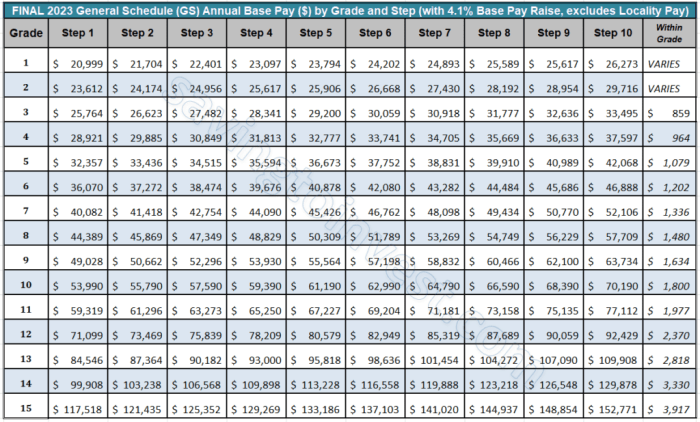
The salary ranges for each GS grade are determined by the General Schedule (GS) pay scale, which is updated annually. The following table provides a general overview of the salary ranges for each GS grade as of 2023:
| GS Grade | Step 1 | Step 10 |
|---|---|---|
| GS-1 | $21,076 | $27,493 |
| GS-2 | $25,698 | $33,493 |
| GS-3 | $30,659 | $40,029 |
| GS-4 | $36,078 | $47,045 |
| GS-5 | $42,033 | $54,625 |
| GS-6 | $48,575 | $62,884 |
| GS-7 | $55,778 | $71,885 |
| GS-8 | $63,683 | $81,702 |
| GS-9 | $72,356 | $92,406 |
| GS-10 | $81,863 | $104,074 |
| GS-11 | $92,278 | $116,778 |
| GS-12 | $103,683 | $130,635 |
| GS-13 | $116,168 | $145,887 |
| GS-14 | $130,000 | $162,732 |
| GS-15 | $145,392 | $181,412 |
Application of GS Pay Raises
GS pay raises are typically applied across different pay grades in a uniform manner. This means that all employees within a specific pay grade will receive the same percentage increase, regardless of their step within that grade. The amount of the pay raise is determined by the annual budget and is typically announced in the spring.
Pay Raise Structure for Different GS Occupations
While the GS pay raise structure is generally uniform, there are some variations in the pay raise structure for different GS occupations. For example, some occupations may have a higher base salary or may receive additional pay for certain qualifications or certifications.
These variations are reflected in the specific pay tables for each occupation.
“The GS pay raise structure is designed to ensure that federal employees are compensated fairly based on their experience, skills, and contributions.”
Wondering about those annual GS pay raises? They can be a bit of a mystery, but don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. Check out this awesome guide, GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources: A Comprehensive Guide , for all the juicy details on the GS pay scale and how it affects your potential raises.
Armed with this knowledge, you can plan for your future, maybe even treat yourself to a celebratory coffee with that raise!
Impact of GS Pay Raises
GS pay raises have a multifaceted impact on the federal government, influencing employee morale, retention, and the overall budget. These raises can be a crucial tool for attracting and retaining a skilled workforce, but they also need to be carefully considered in the context of the government’s financial resources.
Impact on Employee Morale and Retention
GS pay raises can have a significant impact on employee morale and retention. When employees feel fairly compensated for their work, they are more likely to be motivated and engaged. This can lead to increased productivity, improved customer service, and a more positive work environment.
Conversely, stagnant wages can lead to decreased morale, increased turnover, and difficulty attracting and retaining qualified talent.
A study by the Partnership for Public Service found that federal employees are more likely to stay in their jobs if they feel their pay is competitive with the private sector.
Economic Impact of GS Pay Raises
GS pay raises can have a significant impact on the government’s budget. Increased salaries can lead to higher overall spending, which can put pressure on government finances. However, it’s important to consider the potential economic benefits of these raises. A well-compensated federal workforce can contribute to a more robust economy by stimulating spending and supporting local businesses.
The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) estimates that the cost of a 2% pay raise for federal employees would be approximately $4.5 billion.
Implications for Attracting and Retaining Qualified Talent
Attracting and retaining qualified talent is essential for the effective functioning of the federal government. Competitive salaries are a key factor in attracting and retaining a skilled workforce. GS pay raises can help the government stay competitive with the private sector and ensure that it has the talent it needs to meet its mission.
The government is facing a growing challenge in attracting and retaining qualified talent, particularly in STEM fields. Competitive salaries are essential to address this challenge.
Additional Considerations
While the GS pay raise system is generally consistent, it’s important to remember that there are a few additional factors that can influence your annual increase. These factors can add complexity to the process, so understanding them is crucial.
Comparison with Other Federal Pay Systems
Understanding how GS pay raises compare to other federal pay systems helps you assess the overall compensation picture for federal employees.
| Pay System | Description | Typical Pay Raise Structure |
|---|---|---|
| GS | General Schedule | Annual pay raises based on performance and locality adjustments. |
| Senior Executive Service (SES) | Executive-level positions | Performance-based pay with potential for bonuses and other incentives. |
| Foreign Service | Diplomatic and consular service | Annual pay raises based on performance and cost-of-living adjustments. |
| Law Enforcement Officers (LEO) | Federal law enforcement officers | Annual pay raises based on performance and special pay adjustments. |
Average GS Pay Raises Across Geographic Regions
GS pay raises are adjusted based on locality pay, which reflects the cost of living in different areas. This means that pay raises can vary significantly depending on your location.
| Region | Average Annual GS Pay Raise (2023) |
|---|---|
| New York, NY | 3.5% |
| San Francisco, CA | 3.2% |
| Washington, DC | 3.0% |
| Atlanta, GA | 2.8% |
| Dallas, TX | 2.5% |
Impact of GS Pay Raises on Different Salary Levels
The impact of GS pay raises can vary depending on your current salary level. Generally, lower-level GS employees tend to see a larger percentage increase in their pay, while higher-level employees may see a smaller percentage increase.
| GS Grade | Starting Salary (2023) | Estimated Annual Pay Raise (2023) | Percentage Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| GS-5 | $35,000 | $1,400 | 4% |
| GS-11 | $60,000 | $2,400 | 4% |
| GS-14 | $100,000 | $4,000 | 4% |
Conclusion
The GS pay raise system is a dynamic one, with ongoing changes and considerations. As you navigate the complexities of the system, remember that staying informed about your pay raise potential is crucial. By understanding the factors at play and the projected trends, you can make informed decisions about your career path and financial planning.
Whether you’re a seasoned federal employee or just starting out, this information empowers you to advocate for your compensation and secure a rewarding career in the public sector.


