The General Schedule (GS) pay scale is a system used to determine the salaries of federal employees, including those in the field of Human Resources (HR). The GS pay scale is regularly updated to ensure that federal employees are compensated fairly and competitively.
In this article, we will provide an overview of the GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources, including the factors that determine pay grades and steps, the impact of geographic differentials and locality pay, and the benefits and allowances available to federal employees.
The GS pay scale is a complex system, but it is important for HR professionals to understand how it works in order to ensure that they are being compensated fairly. This article will provide you with the information you need to know about the GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources, so that you can make informed decisions about your career.
2024 GS Pay Scale Overview
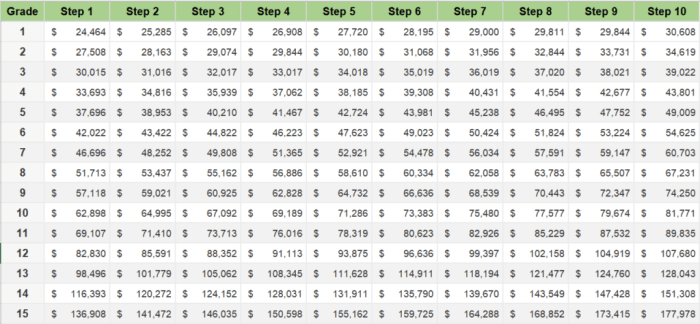
The General Schedule (GS) pay scale is a system used to determine the salaries of federal employees in the United States. The GS pay scale is divided into 15 grades, with each grade further divided into 10 steps. The grade of a position is determined by the level of difficulty and responsibility of the work performed, while the step within a grade is determined by the employee’s length of service and performance.For
2024, the GS pay scale has been updated to reflect changes in the cost of living. The average increase in pay for federal employees is 4.6%. The largest increase is for employees in the lower grades, with those in grades GS-1 through GS-10 receiving an average increase of 5.3%.
Factors Determining GS Pay Grades and Steps
The grade of a GS position is determined by the following factors:
- The level of difficulty and responsibility of the work performed
- The qualifications required for the position
- The level of supervision required
- The impact of the position on the organization
The step within a grade is determined by the following factors:
- The employee’s length of service
- The employee’s performance
- The availability of funds
Changes to the GS Pay Scale for 2024
The following are the key changes to the GS pay scale for 2024:
- The average increase in pay for federal employees is 4.6%.
- The largest increase is for employees in the lower grades, with those in grades GS-1 through GS-10 receiving an average increase of 5.3%.
- The minimum salary for a GS-1, step 1 employee will be $20,681.
- The maximum salary for a GS-15, step 10 employee will be $163,143.
Human Resources GS Pay Scale
The General Schedule (GS) pay scale is used to determine the salaries of federal employees, including those working in human resources (HR). The GS pay scale is based on a combination of factors, including job responsibilities, experience, and location.
Factors Influencing HR Pay
Several factors can influence the pay of HR professionals, including:
-
-*Job responsibilities
HR professionals with more complex and challenging job responsibilities typically earn higher salaries.
-*Experience
HR professionals with more experience typically earn higher salaries.
-*Location
HR professionals working in areas with a higher cost of living typically earn higher salaries.
Range of Pay for HR Professionals
The range of pay for HR professionals can vary significantly depending on the factors mentioned above.
For example, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for HR managers was $126,930 in May 2021. However, the salary range for HR managers can vary from $99,580 to $163,280, depending on factors such as job responsibilities, experience, and location.
Geographic Differentials and Locality Pay
Geographic differentials and locality pay are adjustments to base pay that are designed to compensate employees for the higher cost of living in certain geographic areas. These adjustments are calculated and applied to base pay based on the location of the employee’s duty station.
Locality Pay
Locality pay is a percentage-based adjustment to base pay that is paid to employees who work in geographic areas where the cost of living is significantly higher than the national average. The locality pay percentage is determined by comparing the cost of living in the employee’s duty station to the cost of living in the Washington, D.C.
metropolitan area.For example, an employee who works in San Francisco, California, would receive a locality pay adjustment of 28.18%. This means that their base pay would be increased by 28.18% to compensate for the higher cost of living in San Francisco.
Geographic Differentials
Geographic differentials are adjustments to base pay that are paid to employees who work in geographic areas that are considered to be remote or isolated. The geographic differential percentage is determined by the distance of the employee’s duty station from the nearest metropolitan area.For
example, an employee who works in a remote area of Alaska would receive a geographic differential of 25%. This means that their base pay would be increased by 25% to compensate for the higher cost of living and the challenges of working in a remote location.
Benefits and Allowances
In addition to base pay, federal employees are offered a comprehensive package of benefits and allowances that enhance their overall compensation. These benefits can significantly impact an employee’s financial well-being and quality of life.Health insurance is a core benefit offered to federal employees.
The Federal Employees Health Benefits (FEHB) program provides a wide range of health insurance plans to choose from, allowing employees to select the coverage that best meets their needs and budget. The government contributes a substantial portion of the premium costs, making health insurance more affordable for employees.Retirement
plans are another important benefit for federal employees. The Thrift Savings Plan (TSP) is a tax-advantaged retirement savings plan that offers a variety of investment options. Employees can contribute a portion of their salary to the TSP, and the government matches a percentage of their contributions.
This matching contribution can significantly boost an employee’s retirement savings over time.Paid time off is another valuable benefit offered to federal employees. Employees earn annual leave, sick leave, and other types of paid time off. This allows employees to take time off for vacations, appointments, and other personal needs without losing pay.In
addition to these core benefits, federal employees may also be eligible for a variety of other benefits and allowances, depending on their agency and position. These may include:
- Flexible work schedules
- Telework opportunities
- Tuition assistance
- Professional development opportunities
- Employee assistance programs
- Life insurance
- Disability insurance
Unique Benefits for HR Professionals
HR professionals in the federal government may be eligible for additional benefits and allowances that are specific to their field. These may include:
- Professional certification reimbursement
- Continuing education opportunities
- Leadership development programs
- Networking opportunities
These benefits and allowances can help HR professionals advance their careers and stay up-to-date on the latest trends in human resources management.
Career Progression and Salary Growth
The career path for HR professionals within the federal government typically involves progressive levels of responsibility and leadership. Entry-level positions may include roles such as Human Resources Assistant or Specialist. With experience and strong performance, individuals can advance to roles such as Human Resources Manager, Director of Human Resources, or Chief Human Resources Officer.Promotions
and performance evaluations play a significant role in salary growth for HR professionals. Regular performance evaluations provide opportunities for employees to receive feedback on their work and identify areas for improvement. Promotions to higher-level positions typically come with increased responsibilities and higher pay scales.Training
and development opportunities also contribute to salary growth. The federal government offers various training programs, workshops, and certifications to help HR professionals enhance their skills and knowledge. Acquiring additional qualifications and certifications can make individuals more competitive for promotions and higher-paying positions.Over
time, HR professionals with consistent high performance, a strong work ethic, and a commitment to professional development can experience significant salary growth. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for HR managers in the federal government was $101,490 in May 2022. With experience and career progression, HR professionals can potentially earn salaries well above the median.
Comparison to Private Sector
The GS pay scale for HR professionals is generally comparable to salaries in the private sector, but there are some key differences.In the private sector, HR professionals typically earn higher base salaries than their government counterparts. This is because private companies are often more profit-driven and can afford to pay their employees more.
However, government employees often have better benefits packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.Another factor that contributes to the difference in compensation between the public and private sectors is the level of experience and education required. In the private sector, HR professionals with more experience and education typically earn higher salaries.
In the government, however, salaries are more standardized and based on the employee’s grade level.The job market for HR professionals is competitive in both the public and private sectors. However, the government sector is often seen as a more stable career path, while the private sector offers more opportunities for advancement.
Factors Contributing to Differences in Compensation
*
-*Profitability
Private companies are often more profitable than government agencies, which allows them to pay their employees higher salaries.
-
-*Experience and Education
In the private sector, HR professionals with more experience and education typically earn higher salaries.
-*Benefits
Government employees often have better benefits packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.
-*Job Market
The job market for HR professionals is competitive in both the public and private sectors.
-*Career Path
The government sector is often seen as a more stable career path, while the private sector offers more opportunities for advancement.
Final Thoughts
The GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources is a valuable tool for HR professionals who want to understand their compensation and career progression opportunities. By understanding the factors that determine pay grades and steps, the impact of geographic differentials and locality pay, and the benefits and allowances available to federal employees, HR professionals can make informed decisions about their careers and ensure that they are being compensated fairly.


