In the realm of federal employment, the General Schedule (GS) Pay Scale holds significant sway, shaping the salaries of countless individuals serving in diverse roles. For those occupying positions with unique demands and exceptional responsibilities, the GS Pay Scale for Special Rates offers a tailored compensation structure, ensuring equitable remuneration and recognizing the invaluable contributions of these esteemed professionals.
As we delve into the nuances of the GS Pay Scale 2024 for Special Rates, we will explore its defining characteristics, recent modifications, regional variations, and its profound impact on the federal workforce. By shedding light on this specialized pay scale, we aim to empower federal employees with the knowledge and understanding they need to navigate their career paths and maximize their earning potential.
Definition of GS Pay Scale for Special Rates
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates is a unique pay scale within the federal government’s General Schedule (GS) pay system. It applies to specific occupations that require specialized skills, knowledge, or working conditions that warrant compensation above the standard GS pay grades.
Occupations covered under this pay scale typically involve hazardous or physically demanding work, such as firefighters, police officers, air traffic controllers, and border patrol agents. It also includes occupations with unique expertise, such as nuclear engineers, medical officers, and foreign language specialists.
Purpose and Objectives
The purpose of the GS Pay Scale for Special Rates is to attract and retain highly qualified individuals in critical occupations that require specialized skills or face exceptional challenges. It provides a competitive compensation package to ensure that the federal government can maintain a workforce capable of meeting the demands of these specialized roles.
Changes in GS Pay Scale for Special Rates for 2024
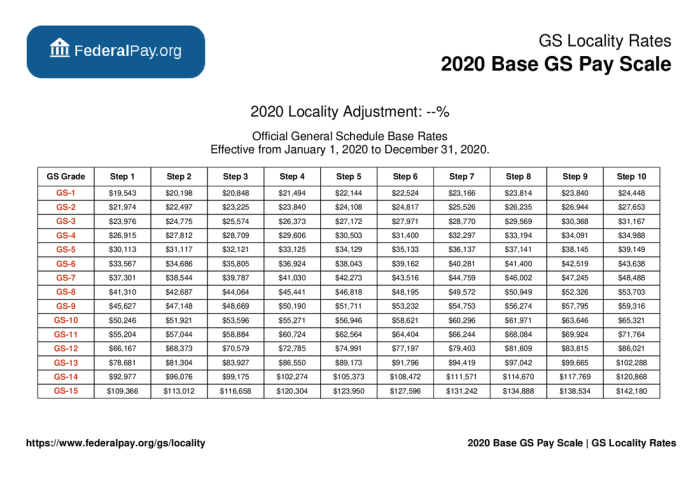
The General Schedule (GS) Pay Scale for Special Rates for 2024 has undergone several modifications compared to previous years. These changes are primarily driven by economic factors, cost of living adjustments, and the need to maintain competitive salaries for specialized positions.
Comparison to Previous Years’ Pay Scales
The 2024 GS Pay Scale for Special Rates reflects an average increase of 4.6% compared to the 2023 pay scale. This increase is slightly higher than the 4.1% increase implemented in 2023. The most significant changes occur in the higher pay grades, with some positions seeing increases of up to 6%.
Factors Influencing the Changes
Several factors have contributed to the changes in the 2024 GS Pay Scale for Special Rates:
- Inflation: Rising inflation rates have eroded the purchasing power of government employees, necessitating salary adjustments to maintain their standard of living.
- Labor Market Conditions: The competitive job market for specialized positions has driven up salaries in the private sector. The government must adjust its pay scales to attract and retain qualified individuals.
- Recruitment and Retention: The government faces challenges in recruiting and retaining employees in certain high-demand occupations. Competitive salaries are essential to address these staffing issues.
Regional Variations in GS Pay Scale for Special Rates
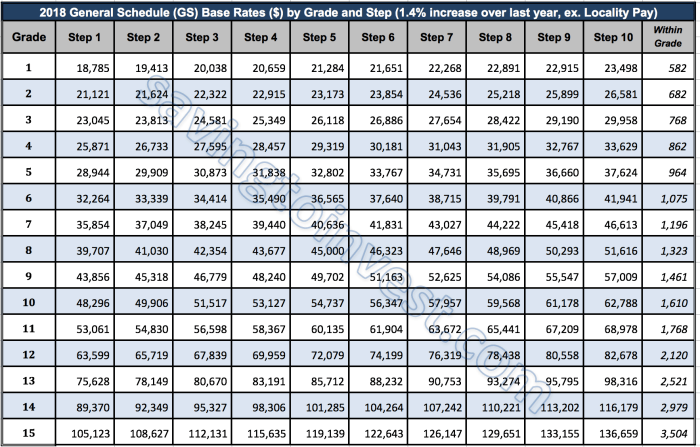
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates varies across different regions within the United States. This variation is primarily due to factors such as the cost of living, local economic conditions, and the availability of skilled labor in each region.
The following table demonstrates the regional variations in the GS Pay Scale for Special Rates:
Pay Scale by Region
| Region | Pay Scale |
|---|---|
| Continental United States | GS-1 to GS-15 |
| Alaska | GS-1 to GS-15, plus 25% |
| Hawaii | GS-1 to GS-15, plus 15% |
| Puerto Rico | GS-1 to GS-15, plus 5% |
| Guam | GS-1 to GS-15, plus 25% |
| American Samoa | GS-1 to GS-15, plus 25% |
| U.S. Virgin Islands | GS-1 to GS-15, plus 15% |
| Northern Mariana Islands | GS-1 to GS-15, plus 25% |
Impact of GS Pay Scale for Special Rates on Federal Employees
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates plays a crucial role in determining the salaries and benefits of federal employees. It establishes a standardized system for compensation, ensuring that employees with similar job responsibilities and qualifications receive fair and equitable pay.The
pay scale influences career advancement by providing a structured path for employees to progress within their field. As employees gain experience and take on additional responsibilities, they can move up the pay scale, earning higher salaries and benefits. This incentivizes employees to develop their skills and seek promotions, fostering a sense of professional growth and satisfaction.The
GS Pay Scale for Special Rates also has a significant impact on the overall federal workforce. By providing competitive salaries and benefits, it attracts and retains talented individuals, ensuring that the government has a skilled and motivated workforce. This ultimately benefits the public, as it allows the government to effectively carry out its functions and provide essential services to the nation.
Impact on Federal Employee Salaries
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates directly affects the salaries of federal employees. Employees are placed into one of 15 pay grades based on their job responsibilities and qualifications. Each pay grade has a minimum, midpoint, and maximum salary.
Employees typically start at the minimum salary for their pay grade and can receive annual pay increases until they reach the maximum salary.The pay scale also includes locality pay adjustments, which are designed to account for the cost of living in different geographic areas.
This ensures that federal employees in high-cost areas, such as major metropolitan areas, receive salaries that are comparable to those of employees in lower-cost areas.
Impact on Career Advancement
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates provides a clear path for career advancement for federal employees. As employees gain experience and take on additional responsibilities, they can move up the pay scale, earning higher salaries and benefits. This incentivizes employees to develop their skills and seek promotions, fostering a sense of professional growth and satisfaction.For
example, an employee who starts as a GS-5 administrative assistant may be eligible for a promotion to GS-7 after two years of service. This promotion would come with a higher salary and more responsibilities, such as supervising other employees or managing projects.
Impact on Federal Workforce
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates plays a vital role in attracting and retaining a skilled and motivated federal workforce. By providing competitive salaries and benefits, the government can ensure that it has the necessary talent to carry out its functions effectively.For
example, the federal government competes with the private sector for talented individuals in fields such as cybersecurity, engineering, and healthcare. By offering competitive salaries and benefits, the government can attract and retain these highly skilled professionals, ensuring that it has the expertise it needs to protect the nation and provide essential services.
Comparison of GS Pay Scale for Special Rates to Other Pay Scales
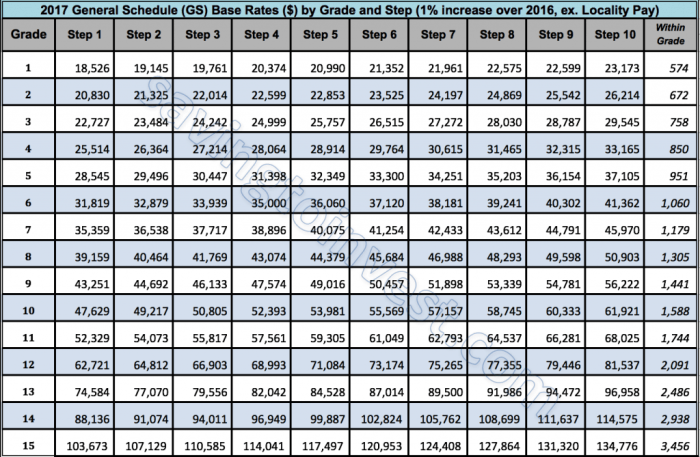
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates is distinct from other pay scales used in the private sector and other government agencies. This section compares the GS Pay Scale for Special Rates to other relevant pay scales, highlighting similarities and differences, as well as the factors that contribute to these variations.
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates is designed to attract and retain highly skilled professionals in specialized fields where there is a shortage of qualified candidates. In contrast, other pay scales, such as the General Schedule (GS) Pay Scale, are used for positions that require less specialized skills and experience.
Private Sector Pay Scales
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates is generally comparable to pay scales in the private sector for similar positions requiring specialized skills and experience. However, there are some key differences between the two pay scales.
- The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates is typically higher than private sector pay scales for entry-level positions.
- The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates has a slower rate of pay increases compared to private sector pay scales.
- The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates includes benefits such as health insurance, retirement benefits, and paid time off, which are often not offered in the private sector.
Other Government Pay Scales
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates is also distinct from other government pay scales, such as the Federal Wage System (FWS) Pay Scale and the Senior Executive Service (SES) Pay Scale.
- The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates is typically higher than the FWS Pay Scale for positions requiring specialized skills and experience.
- The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates is lower than the SES Pay Scale for senior-level executives.
- The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates includes benefits such as health insurance, retirement benefits, and paid time off, which are also offered in other government pay scales.
Factors Contributing to Differences
The differences between the GS Pay Scale for Special Rates and other pay scales are due to several factors, including:
- The level of skills and experience required for the position.
- The availability of qualified candidates in the labor market.
- The funding available for the position.
- The policies and regulations governing the pay scale.
Last Word
The GS Pay Scale for Special Rates stands as a testament to the federal government’s commitment to recognizing and rewarding the exceptional contributions of its employees. Through its carefully calibrated structure and regional adjustments, this pay scale ensures that federal workers are fairly compensated for their expertise and dedication.
As we move forward, it is imperative that we continue to monitor and refine the GS Pay Scale for Special Rates to ensure that it remains an effective tool for attracting and retaining the most talented individuals to serve our nation.


