In the realm of federal employment, the General Schedule (GS) pay scale serves as a cornerstone for determining employee compensation. With the advent of 2024, the GS pay scale has undergone a series of revisions, introducing significant changes to step increases.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the GS Pay Scale 2024, shedding light on the purpose, calculation, and impact of step increases on federal employees’ salaries.
Step increases, an integral component of the GS pay scale, provide a structured mechanism for employees to advance their salaries within their respective grades. These increases are awarded based on a combination of time-in-grade and performance evaluations, offering a clear path for salary growth and career progression.
Step Increases
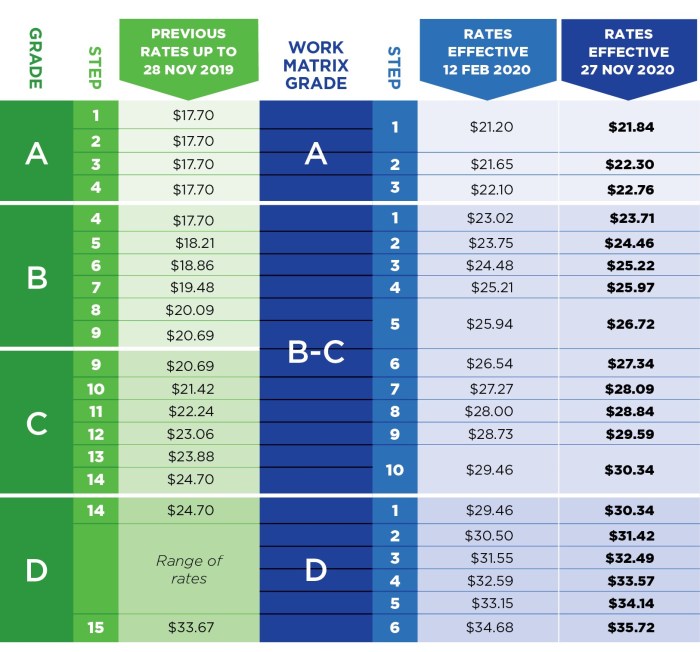
Step increases are a form of pay adjustment within the General Schedule (GS) pay scale, designed to recognize employees’ experience and performance within their grade level.
Step increases are awarded based on two primary factors: time-in-grade and performance. Time-in-grade refers to the amount of time an employee has spent at their current grade level, while performance is evaluated through regular performance appraisals.
Criteria for Moving to the Next Step
- Time-in-Grade: Employees typically move to the next step within their grade after completing a specific amount of time at their current step. This time period varies depending on the grade level, ranging from one to three years.
- Performance: In addition to meeting the time-in-grade requirement, employees must also demonstrate satisfactory or better performance to be eligible for a step increase. Performance is evaluated through regular performance appraisals, which assess factors such as job knowledge, work quality, and productivity.
- Satisfactory Performance: Employees who meet the time-in-grade requirement and receive a satisfactory performance rating are typically eligible for a step increase.
- Outstanding Performance: Employees who exceed expectations and receive an outstanding performance rating may be eligible for an accelerated step increase, which allows them to advance to the next step sooner than the standard time frame.
Calculating Step Increases
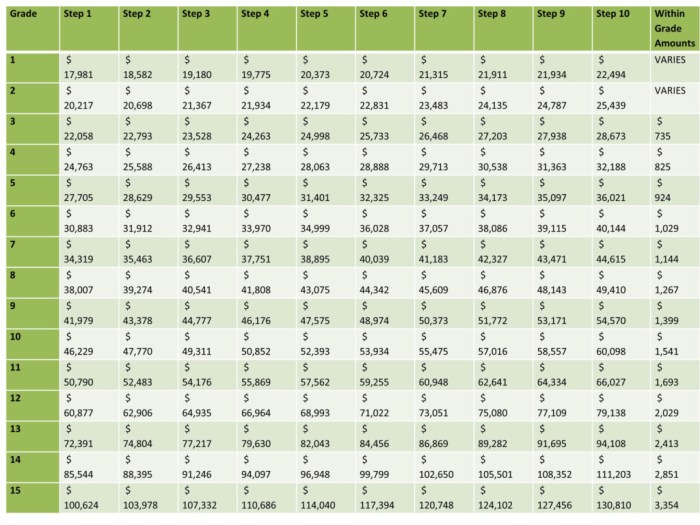
Step increases are calculated using a formula that takes into account the employee’s current step and grade. The formula is as follows:
Step Increase Amount = (Current Step + 1) – Step Increase Percentage
The step increase percentage is determined by the employee’s grade and is published in the General Schedule (GS) pay tables. For example, an employee in grade GS-15 at step 1 would receive a step increase of 3.1%, while an employee in grade GS-7 at step 5 would receive a step increase of 2.4%.
The following table provides an example of how step increases are calculated:
| Current Step | Step Increase Percentage | Step Increase Amount |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.1% | $310 |
| 2 | 2.9% | $290 |
| 3 | 2.7% | $270 |
| 4 | 2.5% | $250 |
| 5 | 2.4% | $240 |
Impact of Step Increases on Salary
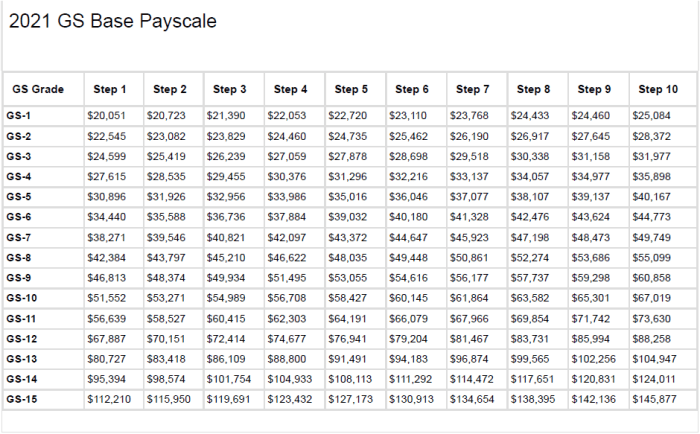
Step increases have a significant impact on an employee’s overall salary. They provide a structured and consistent way for employees to increase their earnings over time, without having to rely solely on promotions or bonuses.Over the course of an employee’s career, step increases can contribute substantially to salary growth.
By moving through the steps within their pay grade, employees can earn progressively higher salaries. This growth can help them keep pace with inflation, maintain their standard of living, and achieve their financial goals.
Salary Progression with Step Increases
The table below illustrates how step increases can contribute to salary progression over time. It assumes an employee starts at the first step of their pay grade and receives an annual step increase of 2%.| Step | Salary ||—|—|| 1 | $50,000 || 2 | $51,000 || 3 | $52,020 || 4 | $53,060 || 5 | $54,120 || 6 | $55,190 || 7 | $56,280 || 8 | $57,390 || 9 | $58,520 || 10 | $59,670 |As shown in the table, an employee who receives regular step increases can experience a significant increase in their salary over time.
After 10 years of service, they would have earned over $59,670, an increase of nearly 20% from their starting salary.
Comparison to Other Pay Systems
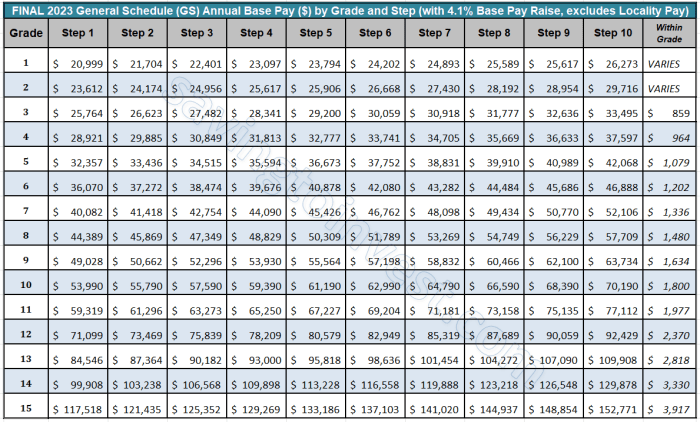
The GS pay scale and step increase system are comparable to other federal and private sector pay systems. In the federal sector, the GS pay scale is similar to the pay scales for other federal employees, such as those in the Senior Executive Service (SES) and the Foreign Service.
In the private sector, the GS pay scale is comparable to the pay scales for employees in similar occupations and industries.One of the key similarities between the GS pay scale and other pay systems is the use of step increases.
Step increases are periodic pay increases that are based on an employee’s length of service in a particular grade. The step increase system is designed to reward employees for their experience and longevity.Another similarity between the GS pay scale and other pay systems is the use of performance-based pay.
Performance-based pay is pay that is based on an employee’s performance. The performance-based pay system is designed to reward employees for their contributions to their organization.One of the key differences between the GS pay scale and other pay systems is the way that pay is determined.
In the GS pay scale, pay is determined by an employee’s grade and step. In other pay systems, pay may be determined by a variety of factors, such as an employee’s job title, experience, and performance.Another key difference between the GS pay scale and other pay systems is the way that step increases are awarded.
In the GS pay scale, step increases are awarded automatically based on an employee’s length of service. In other pay systems, step increases may be awarded based on a variety of factors, such as an employee’s performance or the financial performance of their organization.The
GS pay scale and step increase system have a number of advantages and disadvantages. One of the advantages of the GS pay scale is that it is a transparent system. Employees know exactly how much they will be paid based on their grade and step.
Another advantage of the GS pay scale is that it is a relatively stable system. Pay increases are typically based on an employee’s length of service, rather than on the financial performance of their organization.One of the disadvantages of the GS pay scale is that it can be inflexible.
Employees may not be able to get pay increases if their organization is not performing well financially. Another disadvantage of the GS pay scale is that it can be slow to respond to changes in the market. For example, if the market for a particular occupation is growing, the GS pay scale may not be able to keep up with the demand for employees.Overall,
the GS pay scale and step increase system is a fair and equitable system for compensating federal employees. The system is transparent, stable, and provides employees with opportunities for pay increases based on their length of service and performance.
Policy Updates and Changes
The General Schedule (GS) pay scale and step increase policy are subject to periodic reviews and adjustments to ensure fairness, competitiveness, and alignment with the evolving needs of the federal workforce. Here are some recent and upcoming changes:
In January 2023, the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) announced a 4.6% pay increase for federal employees under the GS pay scale. This increase was part of the broader Federal Employees Pay Comparability Act (FEPCA) adjustment, which aims to maintain pay parity between federal employees and their counterparts in the private sector.
Upcoming Changes
OPM is currently conducting a comprehensive review of the GS pay scale and step increase system. The review aims to address concerns about pay compression, ensure equitable compensation across different occupations and grade levels, and align the pay system with the changing demands of the federal workforce.Based
on the findings of the review, OPM may propose adjustments to the pay scale, step increase structure, or other aspects of the GS pay system. These proposed changes will likely be subject to public comment and review before being implemented.
Last Recap
In conclusion, the GS Pay Scale 2024, with its emphasis on step increases, offers a transparent and merit-based system for federal employee compensation. By understanding the nuances of this pay scale, employees can effectively plan their career trajectories and maximize their earning potential within the federal government.
As the pay scale continues to evolve, it is essential for employees to stay abreast of any policy updates or changes to ensure they remain informed and competitive in the federal workforce.


