Career Progression in the GS Pay System is a roadmap for navigating the intricate world of government employment, offering a structured framework for growth and advancement. It’s a journey that begins with understanding the system’s history, purpose, and key features, and culminates in a fulfilling career trajectory.
The GS Pay System, with its established levels and steps, provides a clear path for employees to progress through their careers, earning higher salaries and acquiring greater responsibilities along the way.
This system, designed to attract and retain talented individuals, offers a unique blend of stability and opportunity. It fosters a culture of continuous learning and development, encouraging employees to hone their skills and expand their knowledge base. From promotions and performance evaluations to training programs and networking opportunities, the GS Pay System provides a comprehensive framework for achieving career goals.
Understanding the intricacies of this system empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their career paths and navigate the various avenues for advancement.
Introduction to the GS Pay System
The GS Pay System, also known as the General Schedule Pay System, is a comprehensive pay structure used by the United States federal government to determine the salaries of its civilian employees. Established in 1949, it has played a crucial role in attracting and retaining a skilled workforce for the government.
The GS Pay System is based on a structured classification system that considers factors like an employee’s education, experience, and the difficulty and responsibility of their job. It aims to ensure fairness and equity in compensation across different government agencies and positions.
Key Features and Principles of the GS Pay System
The GS Pay System is characterized by several key features that contribute to its effectiveness and longevity. These features include:
- Pay Grades and Steps:The system is organized into 15 pay grades, each representing a different level of responsibility and expertise. Within each grade, there are 10 steps, with each step representing an increase in pay based on years of experience and performance.
- Classification System:The GS Pay System utilizes a comprehensive classification system to categorize jobs based on their duties, responsibilities, and required knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs). This ensures that similar positions are compensated fairly, regardless of the agency or location.
- Performance-Based Pay Increases:Employees can receive pay increases based on their performance evaluations. This encourages employees to strive for excellence and contribute to their agency’s success.
- Locality Pay Adjustments:The GS Pay System includes locality pay adjustments to account for differences in the cost of living across different geographic areas. This helps ensure that employees are compensated fairly, regardless of their location.
Role of the GS Pay System in Government Employment
The GS Pay System plays a vital role in government employment by:
- Attracting and Retaining Talent:The system’s structured approach to compensation helps attract and retain qualified individuals by offering competitive salaries and opportunities for advancement. It provides a clear career path for employees, motivating them to develop their skills and contribute to the government’s mission.
- Ensuring Fairness and Equity:The classification system and pay grades ensure that employees are compensated fairly based on their qualifications and responsibilities. This helps maintain a motivated and productive workforce, fostering a culture of respect and equality.
- Promoting Efficiency and Effectiveness:By providing a clear framework for compensation, the GS Pay System promotes efficiency and effectiveness in government operations. It helps ensure that agencies can attract and retain the talent they need to perform their duties effectively.
Understanding Career Progression
Career progression in the GS Pay System is like climbing a ladder, but instead of rungs, you have levels and steps. It’s all about moving up the pay scale and taking on more responsibility as you gain experience and skills.
Levels and Steps in the GS Pay System
The GS Pay System is structured with 15 levels, each divided into 10 steps. Each step represents a higher salary, reflecting your increasing experience and expertise. For example, a GS-5 level has 10 steps, from GS-5/1 to GS-5/10. The higher the step, the higher your salary.
Factors Influencing Career Progression
Career progression in the GS Pay System is influenced by a combination of factors. These factors determine how quickly you move up the ladder and how high you can climb.
- Performance:Your performance is key. Consistently exceeding expectations and demonstrating strong work ethic will earn you recognition and potential for promotion.
- Experience:Gaining relevant experience is crucial. The more experience you have, the more valuable you become to the organization.
- Education:Higher education can open doors to higher levels and more challenging roles.
- Training and Development:Participating in training programs and workshops can enhance your skills and make you a more competitive candidate for promotions.
- Opportunities:Seizing opportunities to take on new responsibilities and projects demonstrates your initiative and willingness to grow.
Pathways to Advancement
The GS Pay System provides a structured framework for career progression, allowing individuals to climb the ranks and advance their careers within the federal government. There are several avenues for career advancement within the GS Pay System, each offering unique opportunities for growth and development.
Promotions
Promotions are the most direct route to advancement within the GS Pay System. Promotions involve moving to a higher grade level, which typically comes with increased responsibilities, authority, and salary. Promotions are usually based on a combination of factors, including:
- Performance: Outstanding performance evaluations demonstrate an individual’s ability to excel in their current role and contribute significantly to their agency’s mission.
- Experience: Gaining experience in different roles and responsibilities within the GS Pay System can showcase versatility and preparedness for a higher-level position.
- Education: Pursuing higher education, such as a master’s degree or specialized certifications, can enhance an individual’s qualifications and make them a more competitive candidate for promotions.
- Training: Participating in relevant training programs and workshops can equip individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in their current role and prepare for future promotions.
Performance Evaluations
Performance evaluations are a crucial component of career progression within the GS Pay System. They provide a formal assessment of an individual’s work performance, identifying areas of strength and areas for improvement. Regular and positive performance evaluations can:
- Boost promotion opportunities: Outstanding performance evaluations serve as evidence of an individual’s capabilities and suitability for higher-level positions.
- Enhance career development: Performance evaluations provide valuable feedback, allowing individuals to identify areas where they can develop their skills and knowledge, ultimately contributing to their career growth.
- Increase salary potential: Strong performance evaluations can lead to higher performance-based pay increases, contributing to an individual’s overall compensation.
Training and Development
Training and development play a critical role in career progression within the GS Pay System. Investing in training and development programs can equip individuals with the skills, knowledge, and experience necessary to advance their careers. These programs can cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Technical skills: Specialized training programs can enhance an individual’s technical expertise, making them more valuable to their agency and opening up opportunities for career advancement.
- Leadership skills: Training programs focusing on leadership development can equip individuals with the skills to manage teams, delegate tasks, and inspire others, preparing them for leadership roles within their agency.
- Management skills: Programs that focus on management skills can enhance an individual’s ability to plan, organize, and supervise, setting them up for success in supervisory or managerial positions.
Examples of Successful Career Progression
“I started my career in the GS Pay System as a GS-5 and, through hard work, dedication, and consistent performance evaluations, I was able to achieve a GS-12 position within 10 years. I actively participated in training programs to develop my skills and knowledge, and I always sought opportunities to take on new responsibilities. My dedication to my work and my commitment to professional development have been instrumental in my career progression within the GS Pay System.”
John Doe, GS-12, Department of Transportation.
“My career journey within the GS Pay System has been marked by a commitment to continuous learning and development. I actively sought opportunities to enhance my skills and knowledge through training programs and workshops. I also made sure to maintain a positive and collaborative work environment, which has helped me build strong relationships with my colleagues and supervisors. My dedication to professional development and my ability to work effectively with others have been key to my advancement within the GS Pay System.”
Career progression in the GS Pay System is a gradual climb, marked by steps of increased responsibility and knowledge. Understanding the intricate structure of this system is key to navigating your path towards advancement. For administrative assistants, a valuable resource is Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrative Assistants , which offers insights into salary ranges and potential growth within the system.
This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your career trajectory, ensuring a steady ascent within the GS Pay System.
Jane Smith, GS-13, Department of Education.
Salary and Benefits: Career Progression In The GS Pay System
The GS Pay System offers a competitive salary structure and a comprehensive benefits package designed to attract and retain talented individuals in the federal government. Understanding the details of the GS Pay System’s salary and benefits is crucial for anyone considering a career in the federal government.
Salary Structure
The GS Pay System is based on a graded system, with 15 grades (GS-1 to GS-15) representing different levels of experience and responsibility. Within each grade, there are 10 steps, which reflect increasing experience and proficiency. The specific salary for a particular grade and step is determined by the employee’s location, which is categorized into different pay areas based on the cost of living.
The salary structure is designed to provide a clear career path with predictable salary increases as employees gain experience and move up the pay scale. This system ensures that employees are compensated fairly for their skills and contributions.
Benefits
The GS Pay System offers a wide range of benefits that are designed to support the well-being of federal employees and their families. These benefits include:
- Health Insurance:Federal employees have access to a variety of health insurance plans, including options for health maintenance organizations (HMOs), preferred provider organizations (PPOs), and fee-for-service plans. The government contributes a significant portion of the premium costs for these plans.
- Retirement:Federal employees are eligible for a defined benefit pension plan, which provides a guaranteed income stream after retirement. The Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS) is the primary retirement plan for most federal employees. In addition to the pension, employees also contribute to a Thrift Savings Plan (TSP), which is a 401(k)-like plan that allows employees to save for retirement on a tax-deferred basis.
- Life Insurance:Federal employees are automatically provided with a basic life insurance policy, and they can purchase additional coverage.
- Paid Leave:Federal employees are entitled to generous paid leave benefits, including vacation time, sick leave, and holidays. The amount of leave available varies depending on the employee’s length of service.
- Disability Insurance:Federal employees are eligible for disability insurance, which provides income protection in the event of a disability.
- Other Benefits:Federal employees may also be eligible for other benefits, such as:
- Long-term care insurance
- Flexible spending accounts
- Employee assistance programs
- Tuition assistance
Comparison to Other Compensation Models, Career Progression in the GS Pay System
The GS Pay System is one of several compensation models used by government agencies and private sector organizations. The GS Pay System is a structured, merit-based system that emphasizes career progression and long-term employment. Compared to other government compensation models, the GS Pay System is known for its stability and predictability.
It offers a clear career path with predictable salary increases. However, some argue that the GS Pay System can be less competitive than other compensation models, particularly in attracting highly skilled professionals who may seek higher salaries or more flexible work arrangements.Compared to private sector compensation models, the GS Pay System typically offers a more comprehensive benefits package, including health insurance, retirement, and paid leave.
However, private sector salaries can be higher in some fields, particularly for those with specialized skills or experience.Ultimately, the best compensation model for an individual depends on their personal priorities and career goals. The GS Pay System is a good option for those seeking a stable career with a comprehensive benefits package, but it may not be the best choice for those seeking the highest possible salary or the most flexibility in their work arrangements.
Navigating the GS Pay System’s ladder of advancement requires a keen understanding of salary ranges and potential for growth. For Human Resources professionals, GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources: A Comprehensive Guide offers a detailed breakdown of the salary structure, allowing you to chart your path towards higher grades and increased compensation.
This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your career progression, setting clear goals and strategizing your journey within the GS Pay System.
Challenges and Considerations
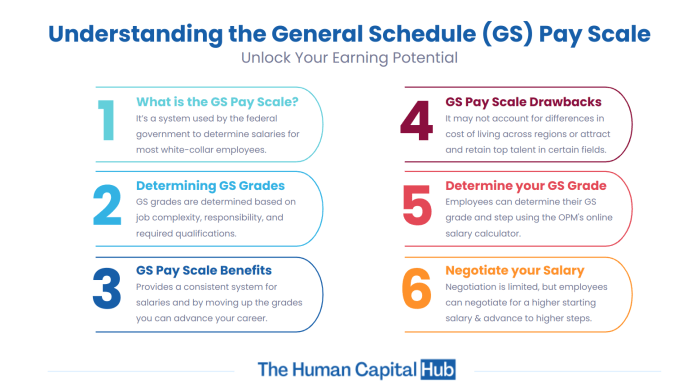
Navigating the GS Pay System for career progression isn’t always a smooth ride. There are hurdles you might encounter, and it’s crucial to be aware of them and equip yourself with the right tools to overcome them.
Networking and Professional Development
Building a strong network and investing in your professional development are vital for career advancement. These aspects significantly impact your chances of landing promotions and opportunities.
- Networking: Connecting with professionals in your field, attending industry events, and engaging in online communities can expose you to valuable insights, potential mentors, and job opportunities. It’s like having a secret weapon, giving you access to hidden opportunities and insider knowledge.
- Professional Development: Continuous learning and upskilling are essential for staying competitive and demonstrating your commitment to growth. Taking courses, attending workshops, earning certifications, or pursuing higher education can significantly enhance your career prospects. Think of it as fueling your career engine, keeping it running smoothly and efficiently.
Strategies for Overcoming Obstacles
Facing challenges is inevitable in any career path. But with the right strategies, you can navigate these obstacles and achieve your career goals.
- Identify and Address Weaknesses: Self-awareness is key. Recognize areas where you might need to improve and develop a plan to address them. Think of it as a personal growth project, focusing on specific areas for improvement.
- Seek Mentorship: Having a mentor who can provide guidance, support, and valuable insights can make a world of difference. Mentors can act as your personal cheerleaders, offering advice and encouragement as you navigate your career journey.
- Stay Informed: Keeping abreast of industry trends, advancements, and changes in the GS Pay System is crucial. This ensures you’re equipped to adapt to new challenges and opportunities. It’s like staying ahead of the curve, anticipating changes and preparing yourself for success.
Resources and Information
Navigating the GS Pay System can be a little overwhelming, especially when you’re looking to climb the career ladder. But don’t worry, there’s a ton of helpful resources out there to guide you!This section provides a rundown of key resources, websites, and information to help you understand career progression within the GS Pay System.
You’ll find everything from official government websites to helpful guides and tools.
Official Government Websites
The official government websites are your go-to sources for accurate and up-to-date information on the GS Pay System. Here are a few you should bookmark:
- OPM (Office of Personnel Management):OPM is the main source for information about the GS Pay System, including pay scales, performance standards, and career development resources. https://www.opm.gov/
- USAJOBS:This website is your one-stop shop for finding federal government jobs, including GS positions. You can search for jobs by location, agency, and s. https://www.usajobs.gov/
- Federal Employee Education and Development (FED):FED provides resources and training opportunities for federal employees, including information on career development and advancement. https://www.fed.gov/
Additional Resources
Beyond official government websites, there are other resources that can provide valuable insights and guidance:
- Professional Organizations:Joining professional organizations related to your field can provide networking opportunities, access to industry publications, and professional development resources.
- Mentors and Coaches:Connecting with mentors or coaches within your agency or field can offer invaluable guidance and support as you navigate your career progression.
- Online Forums and Communities:There are many online forums and communities dedicated to federal employees, where you can connect with others, ask questions, and share experiences.
Career Progression in the GS Pay System
Here’s a table summarizing key information about career progression within the GS Pay System:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Pay Grades | GS Pay System is divided into 15 grades (GS-1 to GS-15), with each grade representing a different level of experience and responsibility. |
| Steps Within a Grade | Each grade has 10 steps, representing incremental increases in pay based on years of service and performance. |
| Promotions | Promotions typically involve moving to a higher GS grade, requiring demonstrated experience, performance, and qualifications. |
| Training and Development | Investing in training and development can enhance your skills and qualifications, making you more competitive for promotions. |
| Performance Management | Strong performance evaluations are crucial for demonstrating your value and potential for advancement. |
Closing Summary
Career Progression in the GS Pay System is a dynamic process, requiring a combination of dedication, skill, and strategic planning. It’s not merely about climbing the ladder; it’s about embracing opportunities, developing expertise, and building a fulfilling career within the government sector.
By understanding the system’s structure, leveraging available resources, and actively pursuing professional development, individuals can unlock their full potential and navigate a rewarding journey of growth and advancement within the GS Pay System.


