GS Pay and Special Rates: Who Qualifies? This question pops up in the minds of many, especially those navigating the complex world of government jobs. It’s like trying to decipher a secret code – who gets the extra cash and why?
Let’s unravel this mystery and find out if you’re eligible for a special rate boost.
Imagine this: you’re working your regular 9-to-5, but you’re also a superhero in disguise. You handle dangerous situations, work in extreme conditions, or maybe you’re just a master of your craft. In the government world, this kind of dedication and skill can translate into special rates, a financial reward for going above and beyond.
But who gets to join the elite squad? What are the qualifications? Buckle up, because we’re about to dive into the nitty-gritty of GS pay and special rates.
Understanding GS Pay and Special Rates: GS Pay And Special Rates: Who Qualifies?
Navigating the world of government salaries can be a complex endeavor, especially when considering the various pay scales and special rates that apply to different roles. This guide will delve into the fundamentals of the General Schedule (GS) pay system and the special rates that supplement it, providing a clearer understanding of how these systems determine government compensation.
GS Pay Structure
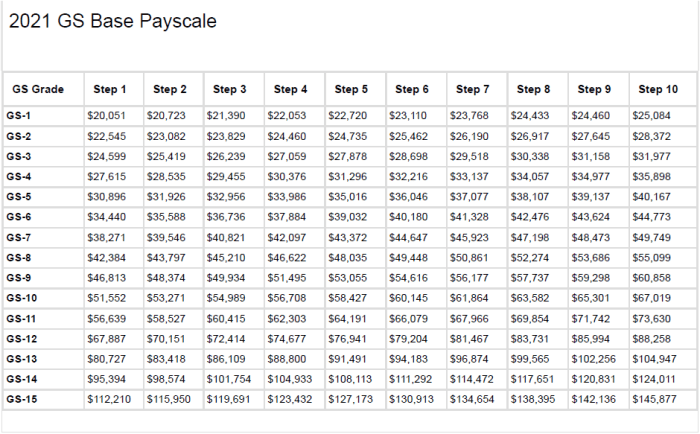
The General Schedule (GS) pay system is the primary method used to determine the salaries of federal employees in the United States. This system establishes a standardized pay scale based on a combination of factors, including:* Grade:Represents the level of responsibility and complexity of the position.
There are 15 GS grades, ranging from GS-1 to GS-15, with higher grades reflecting greater expertise and leadership responsibilities.
Step
Within each grade, there are 10 steps that correspond to an employee’s experience and performance. Employees progress through steps as they gain seniority and demonstrate proficiency.
Locality Pay
This adjustment accounts for regional differences in the cost of living. The government designates specific geographic areas, known as “localities,” and adjusts GS salaries accordingly to ensure competitive compensation in higher-cost areas.
The GS pay system is designed to provide a fair and consistent pay structure for federal employees, ensuring that compensation reflects the level of work performed and the cost of living in the employee’s location.
Special Rates
Special rates are additional payments that can be applied to GS salaries to recognize specific qualifications, responsibilities, or working conditions. These rates are intended to attract and retain qualified personnel in critical positions or to compensate for challenging work environments.
Special rates are often used to address situations where the standard GS pay scale may not adequately reflect the unique demands of certain positions.
Examples of Special Rate Categories
Special rates are categorized based on the specific factors they address. Some common examples include:
- Law Enforcement Special Rates:These rates are used to attract and retain qualified law enforcement officers, recognizing the unique challenges and risks associated with this profession. They may be applied to positions such as police officers, federal agents, and correctional officers.
- Hazardous Duty Special Rates:These rates are used to compensate employees who work in hazardous environments, such as those involving exposure to dangerous chemicals, radiation, or other risks. Examples include positions in the military, environmental protection, and emergency response.
- Recruitment and Retention Special Rates:These rates are used to attract and retain qualified candidates for specific positions where there is a shortage of qualified applicants. They may be applied to positions requiring specialized skills, expertise, or experience.
Eligibility Criteria for Special Rates
Special rates, often referred to as “locality pay” or “cost-of-living adjustments,” are additional payments provided to federal employees working in certain locations to compensate for higher living expenses. These rates are designed to attract and retain qualified individuals in areas with high housing costs, limited job opportunities, or other factors that make it more expensive to live and work.
Job Classification and Duties, GS Pay and Special Rates: Who Qualifies?
The nature of the job and its assigned duties play a significant role in determining eligibility for special rates. The U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM) uses a standardized classification system to categorize federal jobs based on their responsibilities and required skills.
Special rates are often tied to specific job series or occupational categories. For instance, certain engineering or medical positions may qualify for special rates in high-demand areas. The complexity and level of responsibility associated with the job are also considered.
Experience and Training Requirements
In addition to job classification, experience and training requirements can influence eligibility for special rates. Certain positions may necessitate specialized knowledge, certifications, or extensive experience. For example, a position requiring a specific medical license or advanced engineering certification might be eligible for a special rate in areas where such expertise is scarce.
The OPM evaluates the qualifications and experience necessary for a particular position to determine if it warrants a special rate.
Location and Work Environment
The geographic location and work environment are critical factors influencing special rates. Areas with high housing costs, limited job markets, or challenging working conditions are more likely to offer special rates to attract and retain employees. For instance, positions in major metropolitan areas, remote locations, or areas with extreme weather conditions may qualify for special rates.
The OPM considers factors such as the cost of living, housing availability, and the overall desirability of the location when determining special rate eligibility.
The Application Process for Special Rates
Navigating the application process for special rates can feel like walking through a labyrinth, with its intricate steps and required documentation. But, with a clear understanding of the process, it can become a manageable journey.The application process for special rates involves several steps, each requiring careful attention to detail.
Application Submission
The application for special rates is typically submitted through an online portal, requiring the applicant to provide accurate information and supporting documentation. The following steps are essential for a successful application:
- Review the eligibility criteria to ensure you meet the requirements for the specific special rate you are seeking.
- Complete the application form meticulously, providing accurate and up-to-date information.
- Gather and organize all necessary documentation, ensuring it is clear and legible.
- Submit the completed application and supporting documents through the designated online portal or in person at the designated office.
Required Documentation
A comprehensive checklist of required documentation is crucial for a successful application. It ensures that all necessary information is submitted, minimizing the risk of delays or rejection.
- Official transcripts from all educational institutions attended, verifying academic qualifications.
- Current resume or curriculum vitae, highlighting relevant experience and skills.
- Letters of recommendation from supervisors or mentors, vouching for your capabilities and performance.
- Proof of any certifications or licenses required for the specific special rate, demonstrating specialized skills and knowledge.
- Documentation of any relevant work experience, including job descriptions, performance evaluations, or training certificates.
Review and Approval Process
Once submitted, the application undergoes a rigorous review process. The review team assesses the applicant’s qualifications, experience, and documentation against the established criteria for the specific special rate.
So, you’re wondering about GS Pay and Special Rates? Who qualifies? It’s like trying to decipher a secret code, but don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! For a breakdown of the GS Pay Scale in 2024, specifically for administrative assistants, check out Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrative Assistants.
Once you’ve mastered the pay scale, you can conquer the world of GS Pay and Special Rates like a pro, or at least impress your boss with your newfound knowledge.
- The review process typically involves a thorough examination of the applicant’s submitted documentation, including transcripts, resumes, and letters of recommendation.
- The review team may also conduct interviews or background checks to verify information and assess the applicant’s suitability for the special rate.
- The approval process can take several weeks or months, depending on the complexity of the application and the workload of the review team.
Appeal Options
In the event of an unfavorable decision, applicants may have the option to appeal the decision. The appeal process typically involves submitting a formal request for reconsideration, outlining the reasons for the appeal and providing additional supporting documentation.
Navigating the world of GS Pay and Special Rates can feel like trying to decipher a secret code. Who qualifies for what? It’s enough to make your head spin! But fear not, dear HR professional, for there’s a beacon of light in the form of GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources: A Comprehensive Guide.
This handy guide will demystify the complexities of GS Pay and Special Rates, so you can confidently navigate the labyrinthine world of government compensation and make sure your team gets the recognition (and paychecks) they deserve!
- The appeal process is typically governed by specific rules and procedures Artikeld by the relevant agency or organization.
- Applicants should carefully review the appeal guidelines and ensure they meet the requirements for filing an appeal.
- The appeal process may involve a review by a higher-level authority or a formal hearing to present the case for reconsideration.
Benefits and Considerations of Special Rates
Special rates, often referred to as “pay differentials” or “locality pay,” offer a unique set of benefits and considerations for federal employees. These rates aim to attract and retain skilled professionals in specific locations or for specific positions, often compensating for higher costs of living or specialized skills.
Financial Benefits
Special rates can significantly impact an employee’s financial well-being, providing opportunities for salary increases and potential bonuses. These benefits are designed to attract and retain talent, particularly in areas where the cost of living is high or where specialized skills are in high demand.
- Salary Increases: Special rates often translate to higher base salaries compared to standard GS pay scales. This can lead to a substantial increase in an employee’s annual income, providing a financial advantage.
- Bonuses: In some cases, special rates may include performance-based bonuses, offering additional financial incentives for exceptional work. These bonuses can provide a significant boost to an employee’s income, especially during periods of high performance.
Career Advancement Opportunities
While special rates can enhance financial stability, they can also open doors to potential career advancement opportunities. By attracting skilled professionals to specific locations or positions, special rates can create a competitive environment, fostering professional growth and development.
- Specialized Training: Special rates often come with access to specialized training and development programs designed to enhance skills and knowledge. This can lead to increased qualifications and career advancement opportunities.
- Exposure to High-Profile Projects: Positions associated with special rates often involve working on high-profile projects or initiatives, offering valuable experience and exposure to senior leadership. This can enhance career prospects and create opportunities for leadership roles.
Work-Life Balance
Special rates can impact work-life balance in both positive and negative ways. While the financial benefits may provide more flexibility and financial security, the demanding nature of certain positions can lead to longer work hours and increased stress.
Ever wondered if you qualify for those sweet, sweet special rates on top of your GS Pay? Well, buckle up, buttercup, because the world of government pay can be a confusing maze. But fear not! A helpful guide called Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals can help you navigate the labyrinth of GS Pay and special rates, making sure you get every penny you deserve (and maybe even a few extra for a fancy coffee).
So, if you’re an IT professional looking to level up your pay game, this guide is your golden ticket to understanding who qualifies for those special rates and how to make your salary sing.
- Increased Flexibility: The financial security offered by special rates can allow employees to pursue flexible work arrangements, such as telework or compressed workweeks, potentially improving work-life balance.
- Potential for Workload: Positions associated with special rates often come with demanding workloads and high expectations, potentially leading to longer work hours and increased stress. This can impact work-life balance, requiring careful consideration and planning.
Challenges and Limitations
While special rates offer significant benefits, it’s important to acknowledge the potential challenges and limitations associated with these positions.
- Competition: Positions associated with special rates are highly competitive, requiring strong qualifications and experience. The selection process can be rigorous, potentially leading to disappointment for those who do not meet the criteria.
- Limited Availability: Special rates are not available for all positions or locations. The availability of these positions is dependent on agency needs and budgetary considerations.
Resources and Support for GS Pay and Special Rates
Navigating the complexities of GS Pay and special rates can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re seeking guidance and support. Fortunately, a wealth of resources exists to help you understand your rights and options.
Government Websites and Resources
Government websites offer a comprehensive understanding of GS Pay and special rates, including eligibility criteria, pay scales, and application procedures. These resources are invaluable for gaining accurate and up-to-date information:
- Office of Personnel Management (OPM):The OPM is the primary source of information on federal government pay and benefits, including GS Pay and special rates. Visit their website for detailed information on pay scales, eligibility criteria, and application procedures. https://www.opm.gov/
- U.S. Department of Labor (DOL):The DOL provides information on labor laws and regulations, including those related to federal government employment. https://www.dol.gov/
- Federal Register:The Federal Register is the official daily publication for rules, proposed rules, and notices of federal agencies. You can find announcements regarding changes to GS Pay and special rates here. https://www.federalregister.gov/
Contact Information for Relevant Agencies and Organizations
If you have specific questions or require personalized assistance, reaching out to the relevant agencies and organizations is essential.
- OPM Contact Center:For general inquiries about GS Pay and special rates, you can contact the OPM Contact Center by phone at 1-888-782-8883 or by email at [email protected].
- Your Agency’s Human Resources Department:Your agency’s HR department is a valuable resource for questions specific to your organization. They can provide guidance on local policies, application procedures, and other relevant information.
- Federal Employee Education and Assistance Fund (FEEA):FEEA offers financial assistance and support to federal employees and their families. https://www.feea.org/
Additional Resources for Career Guidance and Professional Development
Beyond navigating GS Pay and special rates, seeking career guidance and professional development can enhance your journey in the federal government.
- Federal Executive Institute (FEI):The FEI provides leadership development programs for federal executives. https://www.fei.gov/
- American Society for Public Administration (ASPA):ASPA offers professional development opportunities and resources for public administrators. https://www.aspa.org/
- National Academy of Public Administration (NAPA):NAPA conducts research and provides training to improve the effectiveness of government. https://www.napawash.org/
Epilogue
So, are you ready to unlock the potential of special rates? By understanding the eligibility criteria, navigating the application process, and weighing the benefits and considerations, you can take control of your career and potentially boost your income. Remember, knowledge is power, and in this case, it can lead to a fatter paycheck and a more fulfilling career.
Now go out there, be a government superhero, and get that special rate!


