Understanding the General Schedule (GS) Pay System is crucial for anyone seeking a career in the federal government. This system, established in 1949, provides a structured framework for determining salaries and benefits for millions of federal employees across various agencies and departments.
The GS Pay System is based on a series of pay grades and steps, with each grade representing a specific level of experience and responsibility.
The system is designed to ensure fair compensation and career progression, allowing employees to advance through the ranks as they gain experience and expertise. It’s a complex system with numerous factors influencing pay, including grade, step, experience, education, and performance.
Navigating the GS Pay System can be daunting, but understanding its intricacies is key to maximizing your earning potential and career growth within the federal government.
Introduction to the GS Pay System: Understanding The General Schedule (GS) Pay System
The General Schedule (GS) Pay System is a standardized pay system used by the United States federal government to compensate its civilian employees. It’s a comprehensive system that ensures fair and equitable compensation based on an employee’s experience, education, and the complexity of their job duties.The GS Pay System has been in place since 1949 and has undergone several revisions to adapt to changing economic conditions and the evolving needs of the federal workforce.
Its primary goal is to attract and retain a skilled and diverse workforce by offering competitive salaries and benefits.
Structure and Function
The GS Pay System is structured around a series of grades (GS-1 through GS-15) and steps within each grade. Each grade represents a different level of responsibility and complexity, with higher grades indicating more senior positions. Within each grade, there are 10 steps, which reflect an employee’s experience and performance.
The salary for each GS grade and step is determined by a pay table that is updated annually. The pay table takes into account factors such as location, cost of living, and prevailing wages in the private sector.
“The GS Pay System is a critical component of the federal government’s ability to recruit and retain a highly skilled and qualified workforce.”
Agencies and Organizations Using the GS Pay System
The GS Pay System is used by a wide range of federal agencies and organizations, including:
- Executive Branch departments (e.g., Department of Defense, Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Education)
- Independent agencies (e.g., Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Aviation Administration, National Aeronautics and Space Administration)
- Congressional support agencies (e.g., Library of Congress, Government Accountability Office)
- The Judicial Branch (e.g., Federal Courts, U.S. Marshals Service)
GS Pay Grades and Steps
The General Schedule (GS) pay system is divided into 15 pay grades, each representing a different level of responsibility and experience. Each grade has a specific salary range, and within each grade, there are steps that correspond to increasing levels of experience and performance.
Understanding these grades and steps is crucial for navigating the GS pay system and determining potential salary levels.
Understanding the General Schedule (GS) Pay System can feel like deciphering ancient hieroglyphics, but fear not, intrepid administrative assistants! Navigating the labyrinthine world of GS pay scales is a breeze with this comprehensive guide, Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrative Assistants.
With a little knowledge and this handy resource, you’ll be a GS pay scale pro in no time, ready to command the respect and compensation you deserve.
GS Pay Grades and Salary Ranges
The 15 GS pay grades are numbered from GS-1 to GS-15, with GS-1 being the lowest and GS-15 being the highest. Each grade has a corresponding salary range, which is determined by the locality pay area where the position is located.
Here is a table showing the salary ranges for each GS grade and step in the Washington, D.C. metropolitan area, as of January 2023:
| GS Grade | Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | Step 4 | Step 5 | Step 6 | Step 7 | Step 8 | Step 9 | Step 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS-1 | $32,281 | $33,278 | $34,275 | $35,272 | $36,269 | $37,266 | $38,263 | $39,260 | $40,257 | $41,254 |
| GS-2 | $35,784 | $36,954 | $38,124 | $39,294 | $40,464 | $41,634 | $42,804 | $43,974 | $45,144 | $46,314 |
| GS-3 | $39,685 | $40,987 | $42,289 | $43,591 | $44,893 | $46,195 | $47,497 | $48,799 | $50,101 | $51,403 |
| GS-4 | $44,012 | $45,501 | $47,000 | $48,499 | $49,998 | $51,497 | $52,996 | $54,495 | $55,994 | $57,493 |
| GS-5 | $48,778 | $50,452 | $52,126 | $53,800 | $55,474 | $57,148 | $58,822 | $60,496 | $62,170 | $63,844 |
| GS-6 | $53,999 | $55,856 | $57,713 | $59,570 | $61,427 | $63,284 | $65,141 | $66,998 | $68,855 | $70,712 |
| GS-7 | $59,689 | $61,738 | $63,787 | $65,836 | $67,885 | $69,934 | $71,983 | $74,032 | $76,081 | $78,130 |
| GS-8 | $65,872 | $68,146 | $70,420 | $72,694 | $74,968 | $77,242 | $79,516 | $81,790 | $84,064 | $86,338 |
| GS-9 | $72,588 | $75,122 | $77,656 | $80,190 | $82,724 | $85,258 | $87,792 | $90,326 | $92,860 | $95,394 |
| GS-10 | $79,886 | $82,724 | $85,562 | $88,400 | $91,238 | $94,076 | $96,914 | $99,752 | $102,590 | $105,428 |
| GS-11 | $87,789 | $91,003 | $94,217 | $97,431 | $100,645 | $103,859 | $107,073 | $110,287 | $113,501 | $116,715 |
| GS-12 | $96,351 | $99,953 | $103,555 | $107,157 | $110,759 | $114,361 | $117,963 | $121,565 | $125,167 | $128,769 |
| GS-13 | $105,629 | $109,625 | $113,621 | $117,617 | $121,613 | $125,609 | $129,605 | $133,601 | $137,597 | $141,593 |
| GS-14 | $115,695 | $120,187 | $124,679 | $129,171 | $133,663 | $138,155 | $142,647 | $147,139 | $151,631 | $156,123 |
| GS-15 | $126,585 | $131,651 | $136,717 | $141,783 | $146,849 | $151,915 | $156,981 | $162,047 | $167,113 | $172,179 |
GS Pay Steps
Each GS grade has 10 steps, with Step 1 being the lowest and Step 10 being the highest. Steps represent increasing levels of experience and performance within a particular grade. Employees typically progress through the steps within a grade based on their length of service, performance evaluations, and other factors.The salary increase between steps is generally smaller than the salary increase between grades.
However, the specific salary increase between steps can vary depending on the grade and the locality pay area.
Salary = Base Salary + Locality Pay
Locality pay is an adjustment to the base salary that reflects the cost of living in different geographic areas. It is added to the base salary to compensate for differences in the cost of living across the country.For example, an employee in a GS-5 position in the Washington, D.C.
metropolitan area might start at Step 1 with a salary of $48,778. After a year of satisfactory performance, they might be eligible for a promotion to Step 2, with a salary of $50,452.The exact amount of the salary increase between steps is determined by the General Schedule pay tables, which are updated annually.
The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) publishes these tables, and they are available on the OPM website.
Navigating the General Schedule (GS) Pay System can feel like deciphering ancient hieroglyphics, but fear not! A helpful resource for understanding the 2024 GS pay scale, especially for those in Human Resources, is GS Pay Scale 2024 for Human Resources: A Comprehensive Guide.
This guide will help you make sense of the intricate web of pay grades and steps, ensuring you’re compensated fairly for your hard work and valuable contributions to the workforce.
Determining GS Pay
The General Schedule (GS) pay system uses a complex formula to determine an employee’s salary. Several factors influence the pay grade and step assigned to an employee, including experience, education, and performance.
Factors Influencing GS Pay Grade and Step
Several factors influence the pay grade and step assigned to an employee. These factors include:
- Position Level:The level of difficulty, responsibility, and knowledge required for the position determines the pay grade. Higher-level positions typically fall within higher pay grades.
- Experience:The amount of relevant experience an employee possesses significantly impacts their pay grade and step. Experience is typically measured in years and must be related to the specific job duties of the position.
- Education:The level of education an employee has attained also influences their pay grade and step. Higher levels of education, such as a master’s degree or doctorate, often qualify for higher pay grades.
- Performance:An employee’s performance evaluations can impact their salary progression. Excellent performance can lead to faster promotions within the pay scale, while lower performance may result in slower progression.
- Location:The geographic location of the job can influence pay. Some locations may have higher cost of living adjustments, which can impact the base salary.
- Market Conditions:The competitive job market can influence pay grades and steps. The government may adjust salaries to remain competitive with private sector salaries for similar positions.
The Role of Experience, Education, and Performance
Experience, education, and performance are critical factors in determining an employee’s GS pay grade and step.
- Experience:The GS pay system assigns specific pay steps within each pay grade based on an employee’s experience. For instance, a GS-5 employee with 1 year of experience may start at step 1, while an employee with 5 years of experience may start at step 5.
The more experience an employee has, the higher their starting step within their pay grade.
- Education:A higher level of education can qualify an employee for a higher pay grade. For example, a position requiring a master’s degree may be classified as a GS-7, while a similar position requiring only a bachelor’s degree may be classified as a GS-5.
This means that someone with a master’s degree would start at a higher pay grade and potentially a higher step within that grade.
- Performance:While experience and education are important factors, performance plays a significant role in determining salary progression within the GS system. Employees who consistently exceed expectations can receive promotions within their pay grade or even move to higher pay grades faster.
On the other hand, employees who perform below expectations may experience slower progression or even a reduction in their pay grade.
Examples of How Different Factors Can Impact Starting Salary
Here are some examples of how different factors can impact an employee’s starting salary:
- Example 1:Two individuals apply for a GS-5 position requiring a bachelor’s degree. Candidate A has 2 years of relevant experience, while Candidate B has 5 years of relevant experience. Candidate B is likely to start at a higher step within the GS-5 pay grade due to their greater experience.
- Example 2:Two individuals apply for a GS-7 position requiring a master’s degree. Candidate A has a master’s degree in a related field, while Candidate B has a bachelor’s degree in a related field. Candidate A is likely to start at a higher pay grade due to their higher level of education.
- Example 3:Two individuals are both GS-9 employees with 5 years of experience. Candidate A consistently receives excellent performance evaluations, while Candidate B receives average performance evaluations. Candidate A is likely to receive promotions within the GS-9 pay grade faster than Candidate B, leading to a higher salary over time.
GS Pay Increases and Promotions
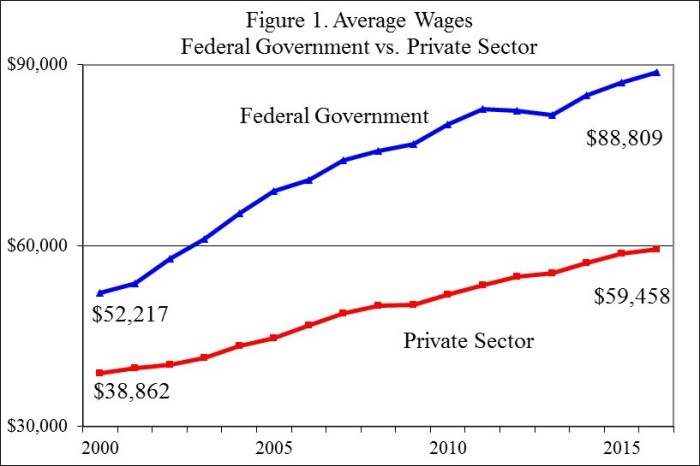
GS employees are eligible for various pay increases throughout their careers. These increases can be based on factors like time in service, performance, or promotions. Understanding these pay increase mechanisms is crucial for GS employees to navigate their career progression and salary expectations.
Annual Step Increases
GS employees are eligible for annual step increases within their pay grade, provided they meet certain criteria. These increases are designed to recognize employees’ experience and growth within their positions.
Understanding the General Schedule (GS) Pay System can be a bit like deciphering a secret code, especially when you’re an IT professional. But fear not, dear techie, for navigating the complexities of the GS Pay Scale 2024 is a breeze with the help of Navigating the GS Pay Scale 2024: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals.
This handy guide will help you unlock the secrets of the GS system, making your salary journey as smooth as a perfectly executed code compilation.
- Eligibility:GS employees are eligible for a step increase after completing a full year of service in their current grade and step.
- Timing:Step increases are typically awarded on the anniversary date of the employee’s initial appointment to their current grade and step.
- Amount:The amount of the step increase varies depending on the employee’s pay grade and step. The step increase amount is predetermined by the General Schedule pay tables.
Performance-Based Raises
Performance-based raises are awarded to GS employees who demonstrate exceptional performance in their roles. These raises recognize and reward employees who consistently exceed expectations.
- Eligibility:Employees are eligible for performance-based raises based on their performance evaluations. The criteria for eligibility and the amount of the raise are determined by the agency and the employee’s performance level.
- Performance Evaluation:The performance evaluation process typically involves a review of the employee’s work performance against established standards and goals.
- Raise Amount:The amount of the performance-based raise is usually tied to the employee’s performance rating. Higher performance ratings generally lead to larger raises.
Promotions
Promotions are a significant career advancement opportunity for GS employees. These promotions recognize employees’ skills, experience, and contributions and involve a move to a higher pay grade.
- Eligibility:Employees are eligible for promotions based on their qualifications, experience, and performance. The specific requirements for promotion vary by position and agency.
- Promotion Process:The promotion process typically involves a competitive selection process. This can include written exams, interviews, or other assessments.
- Pay Increase:Promotions result in a significant pay increase, moving the employee to a higher pay grade and step within the GS system.
Benefits and Perks of the GS Pay System
The General Schedule (GS) pay system offers a comprehensive benefits package to its employees, aiming to attract and retain a skilled workforce in the public sector. These benefits, in addition to the competitive salary, provide financial security and peace of mind to GS employees.
Health Insurance
GS employees have access to a wide range of health insurance plans, including the Federal Employees Health Benefits Program (FEHB). This program offers a variety of plans from different insurance carriers, allowing employees to choose the plan that best meets their needs and budget.
The government contributes a significant portion of the premium cost, making health insurance more affordable for GS employees.
Retirement Plans
GS employees can participate in the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS), a defined-benefit plan that provides a guaranteed monthly pension upon retirement. The FERS also includes a Thrift Savings Plan (TSP), which is a defined-contribution plan similar to a 401(k) plan in the private sector.
The government matches a portion of the employee’s contributions to the TSP, making it a valuable retirement savings option.
Leave
GS employees are entitled to various types of leave, including annual leave, sick leave, and family and medical leave. Annual leave accrues based on length of service and can be used for vacation, personal time, or other purposes. Sick leave can be used for illness or injury, and family and medical leave can be used for childbirth, adoption, or caring for a sick family member.
Other Benefits
GS employees are also eligible for a variety of other benefits, such as:
- Life insurance
- Long-term care insurance
- Disability insurance
- Workers’ compensation
- Employee assistance program
- Tuition assistance
- Childcare assistance
Comparison to Other Pay Systems
The benefits package offered to GS employees is generally considered to be competitive with other pay systems in the public sector. For example, state and local government employees often have similar benefits packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, and leave.
However, the specific benefits and eligibility requirements may vary depending on the employer.
Advantages and Disadvantages, Understanding the General Schedule (GS) Pay System
The GS Pay System offers several advantages for employees, including:
- Competitive salary
- Comprehensive benefits package
- Job security
- Opportunities for advancement
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider, such as:
- Limited opportunities for salary increases
- Bureaucratic procedures
- Potential for political influence
Resources for Understanding the GS Pay System
Navigating the General Schedule (GS) pay system can be overwhelming, but there are several valuable resources available to help you understand its intricacies. Whether you’re a current federal employee seeking information about pay increases or a prospective applicant researching salary expectations, these resources provide comprehensive guidance and official information.
Official Websites and Resources
The official websites of the U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM) and the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) are the primary sources for information about the GS Pay System. These websites provide detailed information on pay grades, steps, benefits, and other relevant aspects of the system.
- U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM):The OPM website provides a wealth of information about the GS Pay System, including pay tables, pay grade descriptions, and information on benefits and retirement. You can access these resources by visiting the OPM website and searching for “General Schedule Pay System.”
- U.S. Department of Labor (DOL):The DOL website provides information on federal labor laws, including the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), which governs minimum wage and overtime pay.
You can access these resources by visiting the DOL website and searching for “Federal Labor Laws.”
Finding Information About Specific Pay Grades, Steps, and Benefits
To find specific information about pay grades, steps, and benefits, you can use the following resources:
- OPM Pay Tables:OPM publishes annual pay tables that show the salary ranges for each GS pay grade and step. These tables are available on the OPM website and are updated each year.
- GS Pay Grade Descriptions:OPM provides detailed descriptions of each GS pay grade, outlining the typical duties and responsibilities associated with each grade.
You can access these descriptions on the OPM website.
- OPM Benefits Information:OPM provides information on the various benefits available to federal employees, including health insurance, retirement plans, and life insurance. You can access this information on the OPM website.
Relevant Publications and Documents
For further research and in-depth understanding, you can refer to the following publications and documents:
- OPM Handbook 5100-1:This handbook provides comprehensive information on the GS Pay System, including pay grade descriptions, pay tables, and information on benefits and retirement.
- OPM Fact Sheets:OPM publishes fact sheets on various aspects of the GS Pay System, such as pay increases, promotions, and benefits.
These fact sheets are available on the OPM website.
- Federal Register:The Federal Register is the official journal of the U.S. government, and it publishes regulations and notices related to the GS Pay System.
Conclusive Thoughts
The GS Pay System offers a stable and rewarding career path for those who choose to serve the nation. By understanding the factors that influence pay, employees can strategically plan their career progression and maximize their earnings. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to advance within the federal government, knowing the ins and outs of the GS Pay System is essential for success.


